N-Dodecyl-N,N-dimethylamine oxide
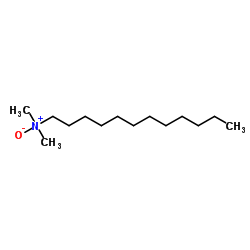
N-Dodecyl-N,N-dimethylamine oxide structure
|
Common Name | N-Dodecyl-N,N-dimethylamine oxide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1643-20-5 | Molecular Weight | 229.402 | |
| Density | 0.996 g/mL at 20ºC | Boiling Point | 100ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H31NO | Melting Point | 132-133ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 94ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Mechanistic insights into the lipid interaction of an ancient saposin-like protein.
Biochemistry 54(9) , 1778-86, (2015) The members of the expanding family of saposin-like proteins (SAPLIPs) have various biological functions in plants, animals, and humans. In addition to a similar protein backbone, these proteins have in common the fact that they interact with lipid membranes.... |
|
|
Modulation of the mitochondrial voltage dependent anion channel (VDAC) by curcumin.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1848(1 Pt A) , 151-8, (2015) Voltage dependent anion channel (VDAC) of mitochondria plays a crucial role in apoptosis. Human VDAC-1, reconstituted in planar lipid bilayer showed reduced conductance when treated with curcumin. Curcumin interacts with residues in the α helical N-terminus o... |
|
|
Chitoporin from the Marine Bacterium Vibrio harveyi: PROBING THE ESSENTIAL ROLES OF TRP136 AT THE SURFACE OF THE CONSTRICTION ZONE.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 19184-96, (2015) VhChiP is a sugar-specific porin present in the outer membrane of the marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi. VhChiP is responsible for the uptake of chitin oligosaccharides, with particular selectivity for chitohexaose. In this study, we employed electrophysiologic... |
|
|
Modulating bilayer mechanical properties to promote the coupled folding and insertion of an integral membrane protein.
Eur. Biophys. J. 44 , 503-12, (2015) Bilayer mechanical properties are not only of crucial importance to the mechanism of action of mechanosensation in lipid membranes but also affect preparative laboratory tasks such as membrane-protein refolding. We report this for coupled refolding and bilaye... |
|
|
Substrate-bound structure of the E. coli multidrug resistance transporter MdfA.
Cell Res. 25 , 1060-73, (2015) Multidrug resistance is a serious threat to public health. Proton motive force-driven antiporters from the major facilitator superfamily (MFS) constitute a major group of multidrug-resistance transporters. Currently, no reports on crystal structures of MFS an... |
|
|
The pilus usher controls protein interactions via domain masking and is functional as an oligomer.
Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 22 , 540-6, (2015) The chaperone-usher (CU) pathway assembles organelles termed pili or fimbriae in Gram-negative bacteria. Type 1 pili expressed by uropathogenic Escherichia coli are prototypical structures assembled by the CU pathway. Biogenesis of pili by the CU pathway requ... |
|
|
Structural basis for self-assembly of a cytolytic pore lined by protein and lipid.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6337, (2015) Pore-forming toxins (PFT) are water-soluble proteins that possess the remarkable ability to self-assemble on the membrane of target cells, where they form pores causing cell damage. Here, we elucidate the mechanism of action of the haemolytic protein fragacea... |
|
|
VDAC3 gating is activated by suppression of disulfide-bond formation between the N-terminal region and the bottom of the pore.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1848 , 3188-96, (2015) The voltage-dependent anion channels (VDACs), VDAC1, VDAC2, and VDAC3, are pore-forming proteins that control metabolite flux between mitochondria and cytoplasm. VDAC1 and VDAC2 have voltage-dependent gating activity, whereas VDAC3 is thought to have weak act... |
|
|
Role of autocleavage in the function of a type III secretion specificity switch protein in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.
MBio 6 , e01459-15, (2015) Type III secretion systems (T3SSs) are multiprotein machines employed by many Gram-negative bacteria to inject bacterial effector proteins into eukaryotic host cells to promote bacterial survival and colonization. The core unit of T3SSs is the needle complex,... |
|
|
A variable DNA recognition site organization establishes the LiaR-mediated cell envelope stress response of enterococci to daptomycin.
Nucleic Acids Res. , (2015) LiaR is a 'master regulator' of the cell envelope stress response in enterococci and many other Gram-positive organisms. Mutations to liaR can lead to antibiotic resistance to a variety of antibiotics including the cyclic lipopeptide daptomycin. LiaR is phosp... |