formycin A
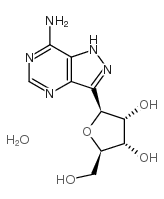
formycin A structure
|
Common Name | formycin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6742-12-7 | Molecular Weight | 285.25700 | |
| Density | 1.771g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 709.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O4 | Melting Point | 153-155ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 382.9ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Purine nucleoside metabolism in the erythrocytes of patients with adenosine deaminase deficiency and severe combined immunodeficiency.
J. Clin. Invest. 57(4) , 1025-35, (1976) Deficiency of erythrocytic and lymphocytic adenosine deaminase (ADA) occurs in some patients with severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID). SCID with ADA deficiency is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. ADA is markedly reduced or undetectable i... |
|
|
The riddle of formycin A insulinotropic action.
Biochem. Mol. Med. 57(1) , 47-63, (1996) Formycin A augments insulin release evoked by glucose (5.6 mm or more), this effect not being rapidly reversible. The mechanism responsible for the insulinotropic action of formycin A was investigated in isolated pancreatic islets. It could not be ascribed to... |
|
|
Tautomerism of the nucleoside antibiotic formycin, as studied by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 95(14) , 4761-2, (1973)
|
|
|
Discovery of novel ribonucleoside analogs with activity against human immunodeficiency virus type 1.
J. Virol. 88(1) , 354-63, (2014) Reverse transcription is an important early step in retrovirus replication and is a key point targeted by evolutionarily conserved host restriction factors (e.g., APOBEC3G, SamHD1). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (RT) is a m... |
|
|
Formycins A and B and some analogues: selective inhibitors of bacterial (Escherichia coli) purine nucleoside phosphorylase.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1120(3) , 239-47, (1992) Formycin B (FB), a moderate inhibitor (Ki approximately 100 microM) of mammalian purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP), and formycin A (FA), which is totally inactive vs. the mammalian enzyme, are both effective inhibitors of the bacterial (Escherichia coli) ... |
|
|
Structure of Escherichia coli 5'-methylthioadenosine/ S-adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase inhibitor complexes provide insight into the conformational changes required for substrate binding and catalysis.
J. Biol. Chem. 278(10) , 8761-70, (2003) 5'-Methylthioadenosine/S-adenosylhomocysteine (MTA/AdoHcy) nucleosidase is a key enzyme in a number of critical biological processes in many microbes. This nucleosidase catalyzes the irreversible hydrolysis of the N(9)-C(1') bond of MTA or AdoHcy to form aden... |