5-Chlorouracil
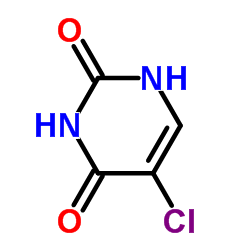
5-Chlorouracil structure
|
Common Name | 5-Chlorouracil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1820-81-1 | Molecular Weight | 146.53 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H3ClN2O2 | Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 203.9ºC | |
|
Electron attachment to chlorouracil: a comparison between 6-ClU and 5-ClU.
J. Chem. Phys. 120 , 704-709, (2004) Low energy electron impact to the isomers 6-chlorouracil (6-ClU) and 5-chlorouracil (5-ClU) yields a variety of negative ion fragments with surprisingly high cross sections. These ions are dominantly formed via sharply structured resonance features at energie... |
|
|
Polymerase incorporation and miscoding properties of 5-chlorouracil.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 740-748, (2010) Inflammation-mediated hypochlorous acid (HOCl) can damage DNA, DNA precursors, and other biological molecules, thereby producing an array of damage products such as 5-chlorouracil (ClU). In this study, we prepared and studied 5-chloro-2'-deoxyuridine (CldU) a... |
|
|
Myeloperoxidase generates 5-chlorouracil in human atherosclerotic tissue: a potential pathway for somatic mutagenesis by macrophages.
J. Biol. Chem. 281(6) , 3096-104, (2006) Somatic mutations induced by oxidative damage of DNA might play important roles in atherogenesis. However, the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. Myeloperoxidase, a heme protein expressed by select populations of artery wall macrophages, initiate... |
|
|
Synthesis and characterization of oligonucleotides containing 5-chlorocytosine.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 17(9) , 1236-44, (2004) Recent studies have shown that reactive chlorine species, derived from myeloperoxidase-mediated inflammation responses, can modify DNA bases, generating 5-chloropyrimidines. The chlorinated adducts could be mutagenic or perturb DNA-protein interactions; howev... |
|
|
5-Chlorouracil, a marker of DNA damage from hypochlorous acid during inflammation. A gas chromatography-mass spectrometry assay.
J. Biol. Chem. 278(35) , 32834-40, (2003) Hypochlorous acid (HOCl), generated from H2O2 and Cl- by myeloperoxidase in activated neutrophils, causes tissue damage during inflammation. We have developed a simple, sensitive (approximately 0.2 fmol on column) and specific GC-MS assay for the detection of... |
|
|
The effect of histidine on the structure and antitumor activity of metal-5-halouracil complexes.
J. Inorg. Biochem. 37(4) , 325-39, (1989) The ternary complexes of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II) ions with 5-halouracils, viz., 5-fluorouracil (5FU), 5-chlorouracil (5ClU), and 5-bromouracil (5BrU), and the biologically important ligand L-histidine (HISD) have been synthesized an... |
|
|
Evaluation of the SOS chromotest for the detection of antimutagens.
Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 17(4) , 258-63, (1991) The SOS chromotest was applied for the detection of antimutagens. To raise SOS induction, the bacteria were treated with the mutagens, UV, 4-nitroquinoline N-oxide (4NQO), N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitroso-guanidine (MNNG), or benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]p). The inhibitory... |
|
|
Electron transfer processes in potassium collisions with 5-fluorouracil and 5-chlorouracil.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13(48) , 21621-9, (2011) Electron transfer to uracil (U), 5-chlorouracil (5-ClU) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) yielding anion formation has been investigated in 30-100 eV potassium-molecule collisions. The rich fragmentation patterns of all three molecules suggest that electron transfer ... |
|
|
Comparative study of HOCl-inflicted damage to bacterial DNA ex vivo and within cells.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 493(2) , 135-42, (2010) The prospects for using bacterial DNA as an intrinsic probe for HOCl and secondary oxidants/chlorinating agents associated with it has been evaluated using both in vitro and in vivo studies. Single-strand and double-strand breaks occurred in bare plasmid DNA ... |
|
|
Base pairing configuration and stability of an oligonucleotide duplex containing a 5-chlorouracil-adenine base pair.
Biochemistry 48(31) , 7539-46, (2009) Inflammation-mediated reactive molecules can damage DNA by oxidation and chlorination. The biological consequences of this damage are as yet incompletely understood. In this paper, we have constructed oligonucleotides containing 5-chlorouracil (ClU), one of t... |