1,4-Oxathiin-3-carboxamide,5,6-dihydro-2-methyl-N-phenyl-, 4,4-dioxide
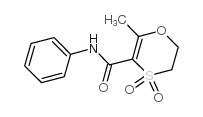
1,4-Oxathiin-3-carboxamide,5,6-dihydro-2-methyl-N-phenyl-, 4,4-dioxide structure
|
Common Name | 1,4-Oxathiin-3-carboxamide,5,6-dihydro-2-methyl-N-phenyl-, 4,4-dioxide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5259-88-1 | Molecular Weight | 267.30100 | |
| Density | 1.392g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 527.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H13NO4S | Melting Point | 128-130℃ (ethanol ) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 272.9ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
The rate of penetration of leaf tissues by the systemic fungicides benodanil (2-iodobenzanilide) and oxycarboxin (2,3-dihydro-6 methyl-5 phenylcarbamoyl-1,4-oxathin-4,4-dioxide).
Beitr. Trop. Landwirtsch. Veterinarmed. 22(1) , 91-4, (1984) Leaf washing after application of benodanil and oxycarboxin reduced the protectant effect more than the eradicant effect. Oxycarboxin penetrated more rapidly than did benodanil . Residues of benodanil (WP) on the leaf surfaces can be absorbed again later in t... |
|
|
[Methods of identifying and determining plantvax and vitavax in water].
Gig. Sanit. (6) , 54-5, (1984)
|
|
|
Degradation of carboxin (Vitavax) and oxycarboxin (Plantvax) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from soil.
J. Environ. Sci. Health B 15(5) , 485-505, (1980) Pseudomonas aeruginosa capable of utilizing carboxin and oxycarboxin as sole sources of carbon and nitrogen was isolated from red sandy loam soil perfused with the solutions of these fungicides. The bacterium hydrolyzed oxycarboxin via the intermediate compou... |