Triflusal
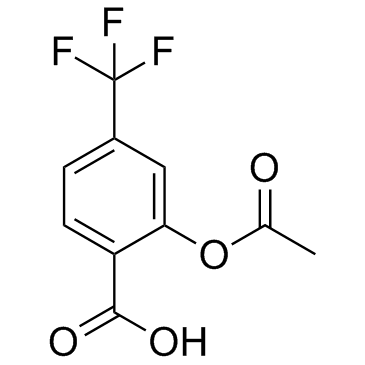
Triflusal structure
|
Common Name | Triflusal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 322-79-2 | Molecular Weight | 248.155 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 316.0±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7F3O4 | Melting Point | 115 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 144.9±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Long-term follow-up of atrial fibrillation patients in the NASPEAF study. Prospective evaluation of different antiplatelet treatments.
Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 62(9) , 992-1000, (2009) In the NASPEAF (National Study for Prevention of Embolism in Atrial Fibrillation) trial, combination therapy with an anticoagulant and an antiplatelet was more effective than anticoagulation alone in patients with atrial fibrillation. We report long-term foll... |
|
|
Electrochemical behavior of triflusal, aspirin and their metabolites at glassy carbon and boron doped diamond electrodes.
Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 13(7) , 569-77, (2010) The electrochemical behavior of triflusal (TRF) and aspirin (ASA), before and after hydrolysis in water and in alkaline medium using two different electrode surfaces, glassy carbon and boron doped diamond, was study by differential pulse voltammetry over a wi... |
|
|
A phase I study to characterize the multiple-dose pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of new enteric-coated triflusal formulations in healthy male volunteers.
Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 7(12) , 1471-9, (2011) An enteric-coated formulation of triflusal (triflusal EC), an antiplatelet agent, was developed to reduce the high incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events (AEs). The aim of this study is to compare the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of tri... |
|
|
Comparative bioavailability study of triflusal oral solution vs. triflusal capsules in healthy subjects. A single, randomized, two-way cross-over, open-label phase I study.
Arzneimittelforschung 60(1) , 36-41, (2010) Triflusal (CAS 322-79-2) is an antiplatelet agent that irreversibly acetylates cyclooxygenase isoform 1 (COX-1) and therefore inhibits thromboxane biosynthesis. The main metabolite of triflusal, 2-hydroxy-4-trifluoromethyl benzoic acid (HTB), possesses also a... |
|
|
Gastrointestinal safety of triflusal solution in healthy volunteers: a proof of concept endoscopic study.
Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 67(7) , 663-9, (2011) Triflusal is an antiplatelet agent that irreversibly acetylates cyclooxygenase isoform 1 (COX-1) and therefore inhibits thromboxane biosynthesis. It was initially marketed as capsules containing 300 mg of active substance. In 2006 a new 600 mg (10 ml) oral so... |
|
|
Triflusal: an old drug in modern antiplatelet therapy. Review of its action, use, safety and effectiveness.
Hellenic J. Cardiol. 50(3) , 199-207, (2009)
|
|
|
Comparison of triple antiplatelet therapy including triflusal and conventional dual therapy in patients who underwent drug-eluting stent implantation.
Int. Heart J. 50(6) , 701-9, (2009) Triflusal is a derivative of acetylsalicylic acid but it exhibits different pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties. The object of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of additional use of triflusal in patients who underwent drug-eluting stent impla... |
|
|
Bioequivalence of two oral formulations of triflusal capsules in healthy volunteers.
Arzneimittelforschung 58(6) , 283-7, (2008) Triflusal (CAS 322-79-2) is an antiplatelet agent related to salicylates used in several European and Latin American countries in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. The aim of this paper was to evaluate the bioequivalence of triflusal derived from two ... |
|
|
Triflusal for preventing serious vascular events in people at high risk.
Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (3) , CD004296, (2005) Aspirin is the standard treatment for secondary prevention of stroke and other vascular events. Several studies suggest that triflusal may have a better safety profile.To determine in people at high risk of vascular events whether triflusal is an effective an... |
|
|
Letter by Borja and Garcia-Rafanell regarding article, "Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association".
Stroke 42(6) , e388; author reply e386, (2011)
|