Bis(4-chlorobenzyl) azodicarboxylate
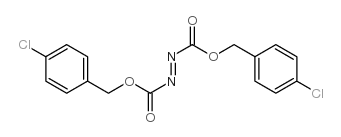
Bis(4-chlorobenzyl) azodicarboxylate structure
|
Common Name | Bis(4-chlorobenzyl) azodicarboxylate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 916320-82-6 | Molecular Weight | 367.18300 | |
| Density | 1.366 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 505.576ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H12Cl2N2O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Druggable glycolytic requirement for Hedgehog-dependent neuronal and medulloblastoma growth.
Cell Cycle 13(21) , 3404-13, (2014) Aberrant activation of SHH pathway is a major cause of medulloblastoma (MB), the most frequent brain malignancy of the childhood. A few Hedgehog inhibitors, all antagonizing the membrane transducer Smo, have been approved or are under clinical trials for the ... |
|
|
Simplification of the Mitsunobu reaction. Di-p-chlorobenzyl azodicarboxylate: a new azodicarboxylate.
Org. Lett. 8 , 5069, (2006) Di-p-chlorobenzyl azodicarboxylate (DCAD) is introduced as a novel, stable, solid alternative to DEAD and DIAD for a variety of Mitsunobu couplings. DCAD/Ph(3)P-mediated reactions in CH(2)Cl(2) generate a readily separable hydrazine byproduct. [reaction: see ... |
|
|
Stimulating effects of a diet negative in dietary cation-anion difference on calcium absorption from the rumen in sheep.
J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl.) 100 , 156-66, (2016) The concept of feeding anionic salts in late gestation is widely used to prevent milk fever in dairy cows. While the effects of these diets on renal Ca excretion and tissue responsiveness towards parathyroid hormone have clearly been demonstrated, data on a p... |
|
|
Quantitative analysis of Hedgehog gradient formation using an inducible expression system.
BMC Dev. Biol. 7 , 43, (2007) The Hedgehog (Hh) family of secreted growth factors are morphogens that act in development to direct growth and patterning. Mutations in human Hh and other Hh pathway components have been linked to human diseases. Analysis of Hh distribution during developmen... |