Ursodiol
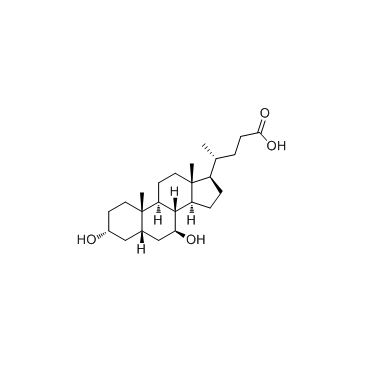
Ursodiol structure
|
Common Name | Ursodiol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 128-13-2 | Molecular Weight | 392.572 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 547.1±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O4 | Melting Point | 203-206 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 298.8±19.7 °C | |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
[Preventive administration of new UDCA derivatives in experimental alcoholic steatohepatitis].
Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 76(1) , 25-9, (2013) We have studied the prophylactic effect of new derivatives of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), including UDCA-N-acetylcysteine, UDCA-L-acetylcysteine, and nor-UDCA (in doses equivalent to 40 mg/kg of UDCA) on the development of experimental alcoholic steatohepati... |
|
|
Primary sclerosing cholangitis, Crohn's disease and HLA-B27 in black South African women.
Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 75(4) , 454-7, (2012) Crohn's disease is rare in South African black people and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is also rare in black patients with IBD, from South Africa. The presence of HLA-B27 is generally associated with seronegative spondylo-arthropathies and correlates ... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoretical molecular descriptors, calculated solely from the mole... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Ultra high resolution SFC-MS as a high throughput platform for metabolic phenotyping: application to metabolic profiling of rat and dog bile.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 966 , 200-7, (2014) Ultra high resolution SFC-MS (on sub-2μm particles) coupled to mass spectrometry has been evaluated for the metabolic profiling of rat and dog bile. The selectivity of the SFC separation differed from that seen in previous reversed-phase UPLC-MS studies on bi... |
|
|
New method for the determination of bile acids in human plasma by liquid-phase microextraction using liquid chromatography-ion-trap-time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1388 , 102-9, (2015) Bile acids (BAs) are derived from cholesterol and produced in the liver. The most abundant bile acids in humans are usually conjugated with glycine and taurine and are divided into primary BAs such as cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and seco... |
|
|
Cytotoxic bile acids, but not cytoprotective species, inhibit the ordering effect of cholesterol in model membranes at physiologically active concentrations.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1828(9) , 2152-63, (2013) Submillimolar concentrations of cytotoxic bile acids (BAs) induce cell death via apoptosis. On the other hand, several cytoprotective BAs were shown to prevent apoptosis in the same concentration range. Still, the mechanisms by which BAs trigger these opposit... |