Sodium chromate anhydrous
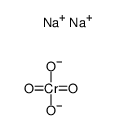
Sodium chromate anhydrous structure
|
Common Name | Sodium chromate anhydrous | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7775-11-3 | Molecular Weight | 161.97300 | |
| Density | 1.483 | Boiling Point | 392ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | CrNa2O4 | Melting Point | 792ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |




GHS05, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Fc Engineering of Human IgG1 for Altered Binding to the Neonatal Fc Receptor Affects Fc Effector Functions.
J. Immunol. 194 , 5497-508, (2015) Engineering of the constant Fc part of monoclonal human IgG1 (hIgG1) Abs is an approach to improve effector functions and clinical efficacy of next-generation IgG1-based therapeutics. A main focus in such development is tailoring of in vivo half-life and tran... |
|
|
Human Skin Cells Are More Sensitive than Human Lung Cells to the Cytotoxic and Cell Cycle Arresting Impacts of Particulate and Soluble Hexavalent Chromium.
Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 166 , 49-56, (2015) Hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) is a known human lung carcinogen, with solubility playing an important role in its carcinogenic potency. Dermal exposure to Cr(VI) is common and has been associated with skin damage; however, no link between chromate exposure and sk... |
|
|
Antibody stabilization of peptide-MHC multimers reveals functional T cells bearing extremely low-affinity TCRs.
J. Immunol. 194(1) , 463-74, (2014) Fluorochrome-conjugated peptide-MHC (pMHC) multimers are commonly used in combination with flow cytometry for direct ex vivo visualization and characterization of Ag-specific T cells, but these reagents can fail to stain cells when TCR affinity and/or TCR cel... |
|
|
Inhibition of CD39 enzymatic function at the surface of tumor cells alleviates their immunosuppressive activity.
Cancer. Immunol. Res. 3(3) , 254-65, (2015) The ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73 hydrolyze extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to generate adenosine, which binds to adenosine receptors and inhibits T-cell and natural killer (NK)-cell responses, thereby suppressing ... |
|
|
The regulatory T cell effector molecule fibrinogen-like protein 2 is necessary for the development of rapamycin-induced tolerance to fully MHC-mismatched murine cardiac allografts.
Immunology 144(1) , 91-106, (2015) Therapies that promote tolerance in solid organ transplantation will improve patient outcomes by eliminating the need for long-term immunosuppression. To investigate mechanisms of rapamycin-induced tolerance, C3H/HeJ mice were heterotopically transplanted wit... |
|
|
Particulate and soluble hexavalent chromium are cytotoxic and genotoxic to human lung epithelial cells.
Mutat. Res. 610(1-2) , 2-7, (2006) Particulate hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) is a well-established human lung carcinogen. It is currently a major public health concern, there is widespread exposure to it in occupational settings and to the general public. However, despite the potential widespre... |
|
|
Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of hexavalent chromium in human and North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) lung cells
Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 150(4) , 487-94, (2009) Humans and cetaceans are exposed to a wide range of contaminants. In this study, we compared the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of a metal pollutant, hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)], which has been shown to cause damage in lung cells from both humans and North ... |
|
|
The clastogenic effects of chronic exposure to particulate and soluble Cr(VI) in human lung cells.
Mutat. Res. 610(1-2) , 8-13, (2006) Hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) is a well-designated human lung carcinogen, with solubility playing an important role in its carcinogenic potential. Although it is known that particulate or water-insoluble Cr(VI) compounds are more potent than the soluble specie... |
|
|
Human lung cell growth is not stimulated by lead ions after lead chromate-induced genotoxicity.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 279(1-2) , 75-84, (2005) Chromate compounds are known human lung carcinogens. Water solubility is an important factor in the carcinogenicity of these compounds with the most potent carcinogenic compounds being water-insoluble or 'particulate'. Previously we have shown that particulat... |
|
|
Comparative cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of particulate and soluble hexavalent chromium in human and sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus) skin cells.
Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 155(1) , 143-50, (2012) Chromium (Cr) is a global marine pollutant, present in marine mammal tissues. Hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] is a known human carcinogen. In this study, we compare the cytotoxic and clastogenic effects of Cr(VI) in human (Homo sapiens) and sperm whale (Physeter... |