capsaicin
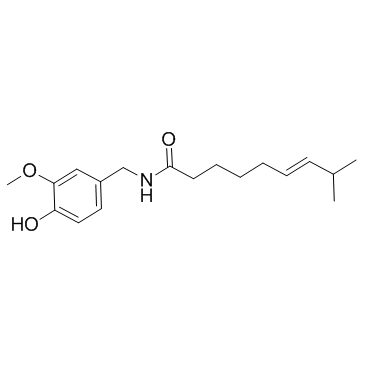
capsaicin structure
|
Common Name | capsaicin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 404-86-4 | Molecular Weight | 305.412 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 469.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H27NO3 | Melting Point | 62-65 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 237.9±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Unbiased classification of sensory neuron types by large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing.
Nat. Neurosci. 18(1) , 145-53, (2015) The primary sensory system requires the integrated function of multiple cell types, although its full complexity remains unclear. We used comprehensive transcriptome analysis of 622 single mouse neurons to classify them in an unbiased manner, independent of a... |
|
|
TCF4 Is a Molecular Target of Resveratrol in the Prevention of Colorectal Cancer.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 10411-25, (2015) The Wnt/β-catenin pathway plays an essential role in the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer. T-cell factor-4 (TCF4) is a member of the TCF/LEF (lymphoid enhancer factor) family of transcription factors, and dysregulation of β-catenin is decisive for the initi... |
|
|
Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide Is Upregulated in Murine Skin Inflammation and Mediates Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid-1-Induced Neurogenic Edema.
J. Invest. Dermatol. 135 , 2209-18, (2015) Although pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) was described as a key vasoregulator in human skin, little is known about its expression in mouse skin. As it is important to investigate PACAP signaling in translational mouse dermatitis mod... |
|
|
Antineoplastic activity of rinvanil and phenylacetylrinvanil in leukaemia cell lines.
Oncol. Lett. 7(5) , 1651-1656, (2014) In the search for novel chemotherapeutic agents for cancer treatment, capsaicin has been shown to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in various types of cancer cell line, including leukaemia cell lines. The capsaicin analogues, rinvanil and phenylacet... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Investigating the potential of under-utilised plants from the Asteraceae family as a source of natural antimicrobial and antioxidant extracts.
Food Chem. 161 , 79-86, (2014) Antimicrobial properties of ethanol and water extracts from eight Asteraceae species were investigated against three Gram positive (Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and Bacillus cereus) and two Gram negative (Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium) bacterial ... |
|
|
Synergism from combinations of tris(benzimidazole) monochloroplatinum(II) chloride with capsaicin, quercetin, curcumin and cisplatin in human ovarian cancer cell lines.
Anticancer Res. 34(10) , 5453-64, (2014) In the present study, synergism in activity from the sequenced combinations of monofunctional platinum tris(benzimidazole)monochloroplatinum(II) chloride (coded as LH4) with capsaicin, quercetin, curcumin and cisplatin was investigated as a function of sequen... |