SR 49059
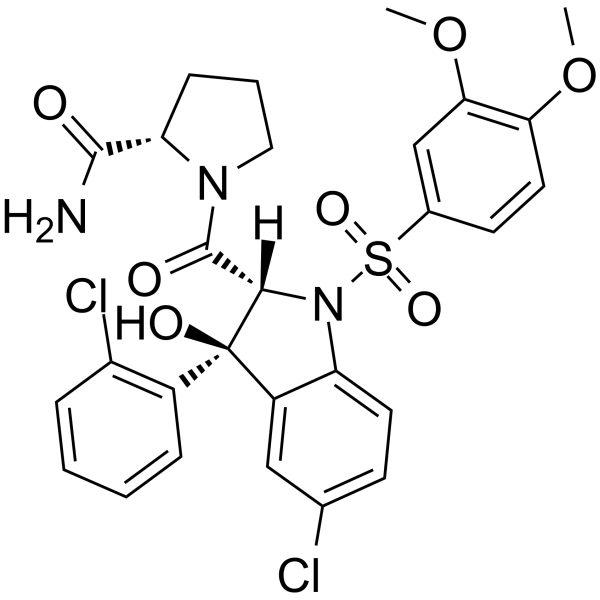
SR 49059 structure
|
Common Name | SR 49059 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 150375-75-0 | Molecular Weight | 620.50 | |
| Density | 1.499g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 868ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H27Cl2N3O7S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 478.8ºC | |
|
The secretion patterns and roles of cardiac and circulating arginine vasopressin during the development of heart failure.
Neuropeptides 51 , 63-73, (2015) The aim of this study is to investigate local cardiac and circulating AVP secretion during heart failure and to determine whether AVP mediates ventricular remodeling.We assessed cardiac function and AVP levels of post-myocardial infarction (MI) heart-failure ... |
|
|
Vasopressin and hydration play a major role in the development of glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis in obese rats.
Diabetologia 58(5) , 1081-90, (2015) High plasma copeptin, a marker of vasopressin (VP) secretion, has been shown to be associated with the metabolic syndrome and development of type 2 diabetes in humans. The present study was designed to determine the long-term influence of plasma VP concentrat... |
|
|
Vasopressin-2 receptor antagonist attenuates the ability of the lungs to clear edema in an experimental model.
Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 47(5) , 583-8, (2012) In the last two decades, the role of the alveolar active sodium transport was extensively studied and was found to play a crucial role in regulating alveolar fluid clearance (AFC), and thus in keeping the airspaces free of edema. The recent development of hig... |
|
|
Pharmacological chaperone activity of SR49059 to functionally recover misfolded mutations of the vasopressin V1a receptor.
J. Biol. Chem. 281(21) , 14604-14, (2006) Pharmacological chaperones represent a new class of ligand with the potential to facilitate the delivery of misfolded, but still active, G-protein-coupled receptors to the cell surface. Using transfected HEK 293T cells, treatment with a nonpeptide antagonist,... |
|
|
Arginine-vasopressin V1a receptor inhibition improves neurologic outcomes following an intracerebral hemorrhagic brain injury.
Neurochem. Int. 58(4) , 542-8, (2011) Cerebral edema is a devastating consequence of brain injury leading to cerebral blood flow compromise and worsening parenchyma damage. In the present study, we investigated the effects of arginine-vasopressin (AVP) V(1a) receptor inhibition following an intra... |
|
|
cAMP/PKA-dependent increases in Ca Sparks, oscillations and SR Ca stores in retinal arteriolar myocytes after exposure to vasopressin.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 51(3) , 1591-8, (2010) To investigate the effects of arginine vasopressin (AVP) on Ca(2+) sparks and oscillations and on sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+) content in retinal arteriolar myocytes.Fluo-4-loaded smooth muscle in intact segments of freshly isolated porcine retinal arte... |
|
|
The cardioprotective effect of different doses of vasopressin (AVP) against ischemia-reperfusion injuries in the anesthetized rat heart.
Peptides 32(12) , 2459-66, (2011) The aim of the present study was to investigate the protective effect of various doses of exogenous vasopressin (AVP) against ischemia-reperfusion injury in anesthetized rat heart. Anesthetized rats were randomly divided into seven groups (n=4-13) and all of ... |
|
|
Effects of YM218, a nonpeptide vasopressin V(1A) receptor-selective antagonist, on vasopressin-induced growth responses in human mesangial cells.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 538(1-3) , 32-8, (2006) Mesangial cells are centrally-located glomerular pericytes with contractile, endocrine, and immunity-regulating functions. These cells are thought to maintain normal glomerular function, since mesangial cell proliferation and extracellular matrix formation ar... |
|
|
Role of vasopressin V(₁A) receptor in the urethral closure reflex in rats.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 300(4) , F976-82, (2011) An enhanced urethral closure reflex via the spinal cord is related to urethral resistance elevation during increased abdominal pressure. However, with the exception of monoamines, neurotransmitters modulating this reflex are not understood. We investigated wh... |
|
|
Oxytocin antagonists for the management of preterm birth: a review.
Am. J. Perinatol. 28(6) , 449-60, (2011) Preterm birth, the leading cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality, is estimated at incidence of 12.7% of all births, which has not decreased over the last four decades despite intensive antenatal care programs aimed at high-risk groups, the widespread use ... |