N-Bromoacetamide
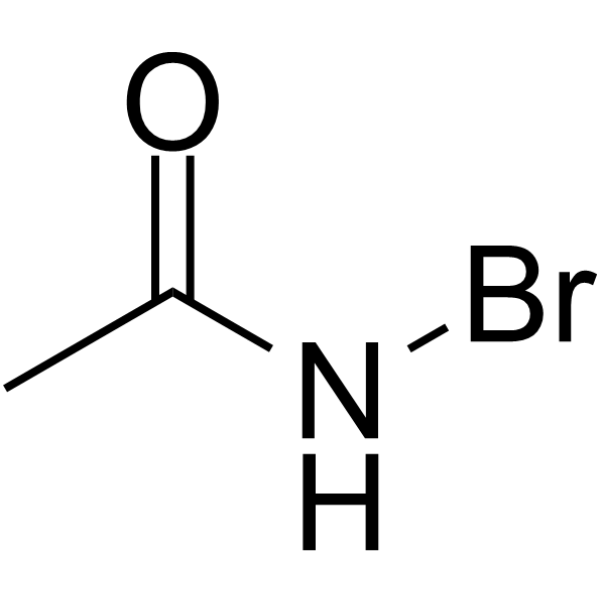
N-Bromoacetamide structure
|
Common Name | N-Bromoacetamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79-15-2 | Molecular Weight | 137.96 | |
| Density | 1.71 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H4BrNO | Melting Point | 102-105°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Mitochondrial function provides instructive signals for activation-induced B-cell fates.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6750, (2015) During immune reactions, functionally distinct B-cell subsets are generated by stochastic processes, including class-switch recombination (CSR) and plasma cell differentiation (PCD). In this study, we show a strong association between individual B-cell fates ... |
|
|
Amino Acid-Derived Metabolites from the Ascidian Aplidium sp.
Mar. Drugs 13 , 3836-48, (2015) Four new iodobenzene-containing dipeptides (1-4), a related bromotryptophan-containing dipeptide (5), and an iodophenethylamine (6) were isolated from the ascidian Aplidium sp. collected off the coast of Chuja-do, Korea. The structures of these novel compound... |
|
|
Aqueous synthesis of N,S-dialkylthiophosphoramidates: design, optimisation and application to library construction and antileishmanial testing.
Org. Biomol. Chem. 11(16) , 2660-75, (2013) We recently reported the use of PSCl3 for the thiophosphorylation of alkylamines where the resulting N-thiophosphoramidate ions could be readily S-alkylated (Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 6156-6158.). Herein we report the development of this methodology using amin... |
|
|
Organo-palladium(II) complexes bearing unsymmetrical N,N,N-pincer ligands: synthesis, structures and oxidatively induced coupling reactions.
Dalton Trans. 44(16) , 7230-41, (2015) The 2-(2′-aniline)-6-imine-pyridines, 2-(C6H4-2′-NH2)-6-(CMe=NAr)C5H3N (Ar = 4-i-PrC6H4 (HL1a), 2,6-i-Pr2C6H3 (HL1b)), have been synthesised via sequential Stille cross-coupling, deprotection and condensation steps from 6-tributylstannyl-2-(2-methyl-1,3-dioxo... |
|
|
O,N,N-pincer ligand effects on oxidatively induced carbon-chlorine coupling reactions at palladium.
Dalton Trans. 44(13) , 6040-51, (2015) The syntheses of two families of sterically tuneable O,N,N pro-ligands are reported, namely the 2-(phenyl-2'-ol)-6-imine-pyridines, 2-(C6H4-2'-OH),6-(CMe=NAr)C5H3N [Ar = 4-i-PrC6H4 (HL1(a)), 2,6-i-Pr2C6H3 (HL1(b))] and the 2-(phenyl-2'-ol)-6-(amino-prop-2-yl)... |
|
|
Brilliant Blue G double staining enhances successful internal limiting membrane peeling with minimal adverse effect by low cellular permeability into live cells.
Retina (Philadelphia, Pa.) 35(2) , 310-8, (2015) Brilliant Blue G is used as a surgical adjuvant for retinal surgery. Although BBG double or multiple staining was reported, the effectiveness and safety of repeated staining is still elusive. To further examine the effectiveness and safety, we examined BBG in... |
|
|
Glucagon-like peptides 1 and 2 and vasoactive intestinal peptide are neuroprotective on cultured and mast cell co-cultured rat myenteric neurons.
BMC Gastroenterol. 12 , 30, (2012) Neuropathy is believed to be a common feature of functional and inflammatory intestinal diseases. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is an acknowledged neuroprotective agent in peripheral, including enteric, and central neurons. The proglucagon-like hormones... |
|
|
RiboTag is a flexible tool for measuring the translational state of targeted cells in heterogeneous cell cultures.
Biotechniques 58 , 308-17, (2015) Primary neuronal cultures are a useful tool for measuring pharmacological- and transgene-regulated gene expression; however, accurate measurements can be confounded by heterogeneous cell types and inconsistent transfection efficiency. Here we describe our ada... |
|
|
Media formulation influences chemical effects on neuronal growth and morphology.
In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 51 , 612-29, (2015) Screening for developmental neurotoxicity using in vitro, cell-based systems has been proposed as an efficient alternative to performing in vivo studies. One tool currently used for developmental neurotoxicity screening is automated high-content imaging of ne... |
|
|
Luteinizing hormone receptors are expressed in rat myenteric neurons and mediate neuronal loss.
Auton. Neurosci. 193 , 104-7, (2015) Clinical observations have suggested repeated gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) exposure to cause intestinal dysfunction and loss of enteric neurons. This has been further studied and confirmed in a rat in vivo model involving iterated GnRH treatments. Me... |