Nutlin-3a
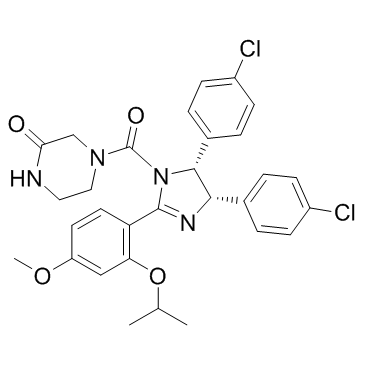
Nutlin-3a structure
|
Common Name | Nutlin-3a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 675576-98-4 | Molecular Weight | 581.490 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H30Cl2N4O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Efficient reactivation of p53 in cancer cells by a dual MdmX/Mdm2 inhibitor.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(52) , 18023-33, (2015) The aberrant interaction between p53 and Mdm2/MdmX is an attractive target for cancer drug discovery because the overexpression of Mdm2 and/or MdmX ultimately impairs the function of p53 in approximately half of all human cancers. Recent studies have shown th... |
|
|
The WIP1 oncogene promotes progression and invasion of aggressive medulloblastoma variants.
Oncogene 34(9) , 1126-40, (2015) Recent studies suggest that medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor of childhood, is comprised of four disease variants. The WIP1 oncogene is overexpressed in Group 3 and 4 tumors, which contain medulloblastomas with the most aggressive clinica... |
|
|
A nanobody modulates the p53 transcriptional program without perturbing its functional architecture.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(20) , 12928-38, (2014) The p53 transcription factor plays an important role in genome integrity. To perform this task, p53 regulates the transcription of genes promoting various cellular outcomes including cell cycle arrest, apoptosis or senescence. The precise regulation of this a... |
|
|
The MDM4/MDM2-p53-IGF1 axis controls axonal regeneration, sprouting and functional recovery after CNS injury.
Brain 138 , 1843-62, (2015) Regeneration of injured central nervous system axons is highly restricted, causing neurological impairment. To date, although the lack of intrinsic regenerative potential is well described, a key regulatory molecular mechanism for the enhancement of both axon... |
|
|
p53 directly activates cystatin D/CST5 to mediate mesenchymal-epithelial transition: a possible link to tumor suppression by vitamin D3.
Oncotarget 6 , 15842-56, (2015) Cystatin D (CST5) encodes an inhibitor of cysteine proteases of the cathepsin family and is directly induced by the vitamin D receptor (VDR). Interestingly, vitamin D3 exerts tumor suppressive effects in a variety of tumor types. In colorectal cancer (CRC) ce... |
|
|
Actinomycin D and nutlin-3a synergistically promote phosphorylation of p53 on serine 46 in cancer cell lines of different origin.
Cell. Signal. 27 , 1677-87, (2015) The p53 tumor suppressor protein is a transcription factor activated by phosphorylation of its N-terminus. MDM2, encoded by a p53-activated gene, acts as a negative-feedback regulator of p53 by promoting p53 degradation. Moreover, MDM2 inhibits p53 by binding... |
|
|
Studying p53 family proteins in yeast: induction of autophagic cell death and modulation by interactors and small molecules.
Exp. Cell Res. 330(1) , 164-77, (2014) In this work, the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae was used to individually study human p53, p63 (full length and truncated forms) and p73. Using this cell system, the effect of these proteins on cell proliferation and death, and the influence of MDM2 and MDMX ... |
|
|
A tryptophanol-derived oxazolopiperidone lactam is cytotoxic against tumors via inhibition of p53 interaction with murine double minute proteins.
Pharmacol. Res. 95-96 , 42-52, (2015) Inactivation of the p53 tumor suppressor protein by interaction with murine double minute (MDM) proteins, MDM2 and MDMX, is a common event in human tumors expressing wild-type p53. In these tumors, the simultaneous inhibition of these interactions with MDMs, ... |
|
|
TP53 Silencing Bypasses Growth Arrest of BRAFV600E-Induced Lung Tumor Cells in a Two-Switch Model of Lung Tumorigenesis.
Cancer Res. 75 , 3167-80, (2015) Lung carcinogenesis is a multistep process in which normal lung epithelial cells are converted to cancer cells through the sequential acquisition of multiple genetic or epigenetic events. Despite the utility of current genetically engineered mouse (GEM) model... |
|
|
Phosphomimetic mutation of the N-terminal lid of MDM2 enhances the polyubiquitination of p53 through stimulation of E2-ubiquitin thioester hydrolysis.
J. Mol. Biol. 427(8) , 1728-47, (2015) Mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) has a phosphorylation site within a lid motif at Ser17 whose phosphomimetic mutation to Asp17 stimulates MDM2-mediated polyubiquitination of p53. MDM2 lid deletion, but not Asp17 mutation, induced a blue shift in the λ(max) of int... |