Congo Red
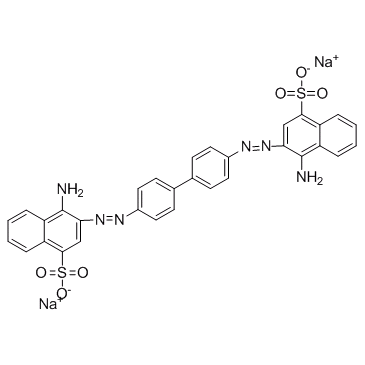
Congo Red structure
|
Common Name | Congo Red | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 573-58-0 | Molecular Weight | 696.663 | |
| Density | 0.995 g/mL at 25 °C | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C32H22N6Na2O6S2 | Melting Point | >360 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
SUMO1 promotes Aβ production via the modulation of autophagy.
Autophagy 11(1) , 100-12, (2015) Autophagy is one of the main mechanisms in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disease. The accumulation of autophagic vacuoles (AVs) in affected neurons is responsible for amyloid-β (Aβ) production. Previously, we reported that SUMO1 (small ubiquitin-li... |
|
|
Swift adsorptive removal of Congo red from aqueous solution by K1.33Mn8O16 nanowires.
J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13(8) , 5452-60, (2013) A swift and efficient approach to converting organic dye effluents into fresh water could be of substantial benefit. In this study, we presented facile hydrothermal synthesis of K1.33Mn8O16 nanowires in ammonium fluoride (NH4F) aqueous solution. The crystalli... |
|
|
Phosphorylation-independent regulation of the diguanylate cyclase WspR.
PLoS Biol. 6 , e67, (2008) Environmental signals that trigger bacterial pathogenesis and biofilm formation are mediated by changes in the level of cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate (c-di-GMP), a unique eubacterial second messenger. Tight regulation of cellular c-di-GMP concentrati... |
|
|
Investigation of preparation conditions and photocatalytic efficiency of nano ZnO using different polysaccharides.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 20(8) , 5654-64, (2013) The development of a complete set of extensive studies combining both the preparation factors of catalysts and photocatalytic experimental factors for the photodegradation of methylene blue, crystal violet, and Congo red using effective nano zinc oxide (ZnO) ... |
|
|
Analysis and testing of biological stains--the Biological Stain Commission Procedures.
Biotech. Histochem. 77(5&6) , 237-275, (2002)
|
|
|
Reconfiguring the quorum-sensing regulator SdiA of Escherichia coli to control biofilm formation via indole and N-acylhomoserine lactones.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75 , 1703-16, (2009) SdiA is a homolog of quorum-sensing regulators that detects N-acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) signals from other bacteria. Escherichia coli uses SdiA to reduce its biofilm formation in the presence of both AHLs and its own signal indole. Here we reconfigured Sdi... |
|
|
Synthesis of tetrahydroxybiphenyls and tetrahydroxyterphenyls and their evaluation as amyloid-β aggregation inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23(6) , 1703-6, (2013) 3,3',4,4'-Tetrahydroxybiphenyl and three isomeric 3,3″,4,4″-tetrahydroxyterphenyls with varying geometries around the central phenyl ring have been synthesized and evaluated for their in vitro activity against aggregation of Alzheimer's amyloid-β peptide (Aβ)... |
|
|
A 3D human neural cell culture system for modeling Alzheimer's disease.
Nat. Protoc. 10(7) , 985-1006, (2015) Stem cell technologies have facilitated the development of human cellular disease models that can be used to study pathogenesis and test therapeutic candidates. These models hold promise for complex neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), beca... |
|
|
Synthesis, characterization and potential applications of multifunctional PEO-PPOPEO- magnetic drug delivery system.
Curr. Med. Chem. 19(30) , 5199-204, (2012) Magnetic nanocomposites (MNCs) have highly been acknowledged in the diagnostics and therapeutic applications. Particularly, the multifunctional MNCs have brought a variety of possibilities in targeted drug delivery as well as non-invasive multimodality imagin... |
|
|
Relevant role of fibronectin-binding proteins in Staphylococcus aureus biofilm-associated foreign-body infections.
Infect. Immun. 77(9) , 3978-91, (2009) Staphylococcus aureus can establish chronic infections on implanted medical devices due to its capacity to form biofilms. Analysis of the factors that assemble cells into a biofilm has revealed the occurrence of strains that produce either a polysaccharide in... |