3-(Trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid
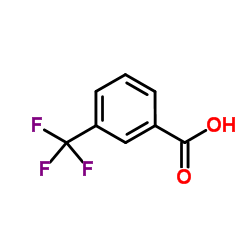
3-(Trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 3-(Trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 454-92-2 | Molecular Weight | 190.119 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 237.7±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H5F3O2 | Melting Point | 104-106 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 102.9±27.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
The many roles for fluorine in medicinal chemistry.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 4359-69, (2008)
|
|
|
Studies on the metabolism of fluorinated xenobiotics in the rat using 19F-NMR and 1H-NMR spectroscopy.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 8(8-12) , 939-44, (1990)
|
|
|
Bacterial metabolism of side chain fluorinated aromatics: cometabolism of 3-trifluoromethyl(TFM)-benzoate by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2 and Rhodococcus rubropertinctus N657.
Arch. Microbiol. 149(3) , 188-97, (1988) The TOL plasmid-encoded enzymes of the methylbenzoate pathway in Pseudomonas putida mt-2 cometabolized 3-trifluoromethyl (TFM)-benzoate. Two products, 3-TFM-1,2-dihydroxy-2-hydrobenzoate (3-TFM-DHB) and 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-7,7,7-trifluoro-hepta-2,4-dienoate (7-TF... |
|
|
Degradation of meta-trifluoromethylbenzoate by sequential microbial and photochemical treatments.
FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 110(2) , 213-6, (1993) m- and p-trifluoromethyl (TFM)-benzoates are incompletely degraded by aerobic bacteria that catabolize alkylbenzoates; biodegradation ceases after ring-fission with the accumulation of a trifluoromethyl muconate semialdehyde (2-hydroxy-6-oxo-7,7,7-trifluorohe... |
|
|
Regioselective dioxygenation of ortho-trifluoromethylbenzoate by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 142: evidence for 1,2-dioxygenation as a mechanism in ortho-halobenzoate dehalogenation.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 213(3) , 759-67, (1995) Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 142 oxidizes 2-halobenzoates via a multicomponent oxygenase (V. Romanov and R.P. Hausinger, J. Bacteriol., 1994, 176(11), 3368-3374). The intermediacy of a highly unstable cis-diol in the reaction has been proposed. Direct eviden... |
|
|
Polymeric drugs with prolonged sustained delivery of specific anti-aggregant agents for platelets: kinetic analysis of the release mechanism.
J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 15(7) , 917-28, (2004) The in vitro aqueous behaviour of a metacryloyloxyethyl [2-(acetyloxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)]benzoate (THEMA)/N,N'-dimethylacrylamide (DMA) copolymer with a THEMA molar content of 39% (labeled THDMA39) has been investigated. This composition has been selected t... |
|
|
Dissociation constants of neutral and charged acids in methyl alcohol. The acid strength resolution. Rived F, et al.
Anal. Chim. Acta 374(2) , 309-324, (1998)
|
|
|
Solubility of fluorinated pharmaceuticals in dense carbon dioxide. Laitinen A, et al.
Org. Process Res. Dev. 4(5) , 353-6, (2000)
|