Safranin
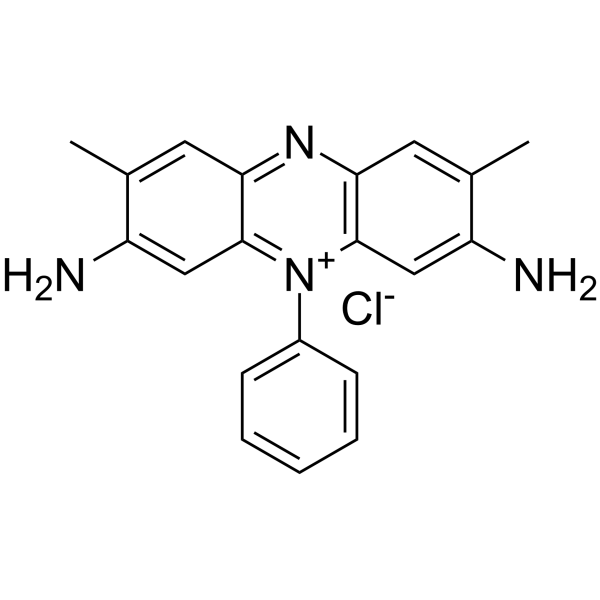
Safranin structure
|
Common Name | Safranin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 477-73-6 | Molecular Weight | 350.845 | |
| Density | 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H19ClN4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 46 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Driving cartilage formation in high-density human adipose-derived stem cell aggregate and sheet constructs without exogenous growth factor delivery.
Tissue Eng. Part A 20(23-24) , 3163-75, (2014) An attractive cell source for cartilage tissue engineering, human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs) can be easily expanded and signaled to differentiate into chondrocytes. This study explores the influence of growth factor distribution and release kinetics o... |
|
|
In vitro characterization of self-assembled anterior cruciate ligament cell spheroids for ligament tissue engineering.
Histochem. Cell Biol. 143(3) , 289-300, (2015) Tissue engineering of an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) implant with functional enthesis requires site-directed seeding of different cell types on the same scaffold. Therefore, we studied the suitability of self-assembled three-dimensional spheroids generat... |
|
|
C-phycocyanin prevents cisplatin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 406 , 183-97, (2015) The potential of C-phycocyanin (C-PC) to prevent cisplatin (CP)-induced kidney mitochondrial dysfunction was determined in CD-1 male mice. The CP-induced mitochondrial dysfunction was characterized by ultrastructural abnormalities and by decrease in the follo... |
|
|
Role of the Mmr efflux pump in drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57(2) , 751-7, (2013) Efflux pumps are membrane proteins capable of actively transporting a broad range of substrates from the cytoplasm to the exterior of the cell. Increased efflux activity in response to drug treatment may be the first step in the development of bacterial drug ... |
|
|
Characterization of adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction for clinical application to cartilage regeneration.
In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 51(2) , 142-50, (2015) Bone marrow concentration (BMC) is the most recognized procedure to prepare mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration. However, bone marrow aspiration is highly invasive and results in low stem cell numbers. Recently, adipose tissue-derived stromal va... |
|
|
Conditioned medium as a strategy for human stem cells chondrogenic differentiation.
J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9 , 714-23, (2015) Paracrine signalling from chondrocytes has been reported to increase the synthesis and expression of cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) by stem cells. The use of conditioned medium obtained from chondrocytes for stimulating stem cells chondrogenic different... |
|
|
Extracellular Calcium Modulates Chondrogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: A Novel Approach for Osteochondral Tissue Engineering Using a Single Stem Cell Source.
Tissue Eng. Part A 21 , 2323-33, (2015) We have previously shown that elevating extracellular calcium from a concentration of 1.8 to 8 mM accelerates and increases human adipose-derived stem cell (hASC) osteogenic differentiation and cell-mediated calcium accretion, even in the absence of any other... |
|
|
Dye removal by surfactant encapsulated polyoxometalates
J. Hazard. Mater. 280 , 428-35, (2014) A novel surfactant encapsulated polyoxometalate (SEP) has been synthesized by using a simple ion-exchange reaction. The prepared SEP complex was found to self-assemble into nanospherical particles whose morphology and component were characterized by TEM and X... |
|
|
Inhibition of 5-LOX, COX-1, and COX-2 increases tendon healing and reduces muscle fibrosis and lipid accumulation after rotator cuff repair.
Am. J. Sports Med. 42(12) , 2860-8, (2014) The repair and restoration of function after chronic rotator cuff tears are often complicated by muscle atrophy, fibrosis, and fatty degeneration of the diseased muscle. The inflammatory response has been implicated in the development of fatty degeneration af... |
|
|
Eupatilin ameliorates collagen induced arthritis.
J. Korean Med. Sci. 30(3) , 233-9, (2015) Eupatilin is the main active component of DA-9601, an extract from Artemisia. Recently, eupatilin was reported to have anti-inflammatory properties. We investigated the anti-arthritic effect of eupatilin in a murine arthritis model and human rheumatoid synovi... |