2,3,6-Trimethylphenol
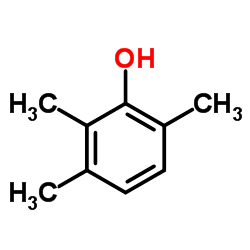
2,3,6-Trimethylphenol structure
|
Common Name | 2,3,6-Trimethylphenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2416-94-6 | Molecular Weight | 136.191 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 223.0±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12O | Melting Point | 59-62 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 100.0±8.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Photodynamic activation as a molecular switch to promote osteoblast cell differentiation via AP-1 activation.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 13114, (2015) In photodynamic therapy (PDT), cells are impregnated with a photosensitizing agent that is activated by light irradiation, thereby photochemically generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). The amounts of ROS produced depends on the PDT dose and the nature of ... |
|
|
Hypercalcemia Leads to Delayed Corneal Wound Healing in Ovariectomized Rats.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38 , 1063-9, (2015) Hypercalcemia is often observed in postmenopausal women as well as in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism or malignant tumors. In this study, we investigated the relationship between calcium ion (Ca(2+)) levels in lacrimal fluid and the rate of corneal ... |
|
|
Oncostatin M Promotes Osteoblastic Differentiation of Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Through JAK3-STAT3 Pathway.
J. Cell. Biochem. 116 , 1325-33, (2015) Vascular calcification is a clinically significant component of atherosclerosis and arises from chronic vascular inflammation. Oncostatin M (OSM) derived from plaque macrophages may contribute to the development of atherosclerotic calcification. Here, we inve... |
|
|
Palmitic acid induces osteoblastic differentiation in vascular smooth muscle cells through ACSL3 and NF-κB, novel targets of eicosapentaenoic acid.
PLoS ONE 8 , e68197, (2013) Free fatty acids (FFAs), elevated in metabolic syndrome and diabetes, play a crucial role in the development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) counteracts many aspects of FFA-induced vascular pathology. Although vascul... |