(−)-trans-Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol
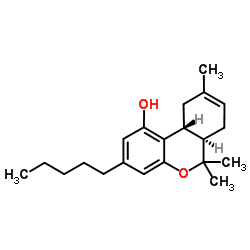
(−)-trans-Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol structure
|
Common Name | (−)-trans-Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5957-75-5 | Molecular Weight | 314.462 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 383.5±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H30O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 144.5±22.1 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Effects of cannabinoids in membrane bilayers containing cholesterol.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1420(1-2) , 252-65, (1999) The thermotropic and dynamic properties of the biologically active Delta(8)-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta(8)-THC) and its inactive congener O-methyl-Delta(8)-tetrahydrocannabinol (Me-Delta(8)-THC) in DPPC/cholesterol (CHOL) bilayers have been studied using a co... |
|
|
Receptor mechanism and antiemetic activity of structurally-diverse cannabinoids against radiation-induced emesis in the least shrew.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 563(1-3) , 187-96, (2007) Xenobiotic cannabinoid CB1/CB2-receptor agonists appear to possess broad-spectrum antiemetic activity since they prevent vomiting produced by a variety of emetic stimuli including the chemotherapeutic agent cisplatin, serotonin 5-HT3-receptor agonists, dopami... |
|
|
Loss of THCCOOH from urine specimens stored in polypropylene and polyethylene containers at different temperatures.
J. Anal. Toxicol. 24(7) , 567-71, (2000) The loss of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THCCOOH) from urine specimens stored in polypropylene and polyethylene containers at 4 degrees C and 25 degrees C was examined. All specimens were analyzed by GC-MS after sampling at various times over a one-week perio... |
|
|
Characterisation of the rat cerebella CB1 receptor using SR141716A, a central cannabinoid receptor antagonist.
Neurosci. Lett. 220(2) , 101-4, (1996) We describe the use of SR141716A, a central cannabinoid antagonist, in radioligand binding and adenylyl cyclase (AC) inhibition studies in rat cerebella membranes. The binding of [3H]SR141716A was dose-dependent and saturable, with Kd and Bmax of 0.61 +/- 0.1... |
|
|
Cannabinoids inhibit cellular respiration of human oral cancer cells.
Pharmacology 85(6) , 328-35, (2010) The primary cannabinoids, Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta(9)-THC) and Delta(8)-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta(8)-THC) are known to disturb the mitochondrial function and possess antitumor activities. These observations prompted us to investigate their effec... |
|
|
Human skin permeation of Delta8-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and cannabinol.
J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 56(3) , 291-7, (2004) The purpose of this study was to quantify the in-vitro human skin transdermal flux of Delta8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta8-THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabinol (CBN). These cannabinoids are of interest because they are likely candidates for transdermal combi... |
|
|
Variation of the alkyl side chain in delta 8-THC.
Life Sci. 56(23-24) , 2021-4, (1995) The synthesis of (2'RS)-2'-methyl-, (3'RS)-, (3'S)-3'-methyl-, and 4'-methyl-delta 8-THC has been carried out, and the pharmacology of all four compounds has been investigated. All four compounds showed typical cannabinoid activity both in vitro and in vivo. ... |
|
|
Cannabinoid photolabelling of a G-protein gamma-subunit in mouse peritoneal cells.
Life Sci. 56(23-24) , 1991-8, (1995) Binding and photoactivation of a cannabinoid-derived ligand to intact mouse peritoneal cells has resulted in the labelling of a G-protein gamma-subunit. The assignment of structure is based on the product's physical characteristics and its ability to react wi... |
|
|
Enhanced solubility, stability, and transcorneal permeability of δ-8-tetrahydrocannabinol in the presence of cyclodextrins.
AAPS PharmSciTech 12(2) , 723-31, (2011) The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of cyclodextrins (CDs) on aqueous solubility, stability, and in vitro corneal permeability of delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ(8)-THC). Phase solubility of Δ(8)-THC was studied in the presence of 2-hydrox... |
|
|
The role of halogen substitution in classical cannabinoids: a CB1 pharmacophore model.
AAPS J. 6(4) , e30, (2004) The presence of halogens within the classical cannabinoid structure leads to large variations in the compounds' potencies and affinities for the CB1 receptors. To explore the structure activity relationships within this class of analogs we have used a series ... |