1-Isothiocyanatobutane
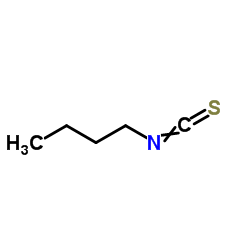
1-Isothiocyanatobutane structure
|
Common Name | 1-Isothiocyanatobutane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 592-82-5 | Molecular Weight | 115.197 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 168.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NS | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 66.1±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
In vitro metabolic conversion of the organic breakdown products of glucosinolate to goitrogenic thiocyanate anion.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95 , 2244-51, (2015) Glucosinolates are abundant in Brassicaceae vegetables, and they are degraded into various organic breakdown products (BPs) (R-CN, -NCS and -SCN) by myrosinase when plant tissues are damaged. This study was designed to investigate whether these BPs could be b... |
|
|
Nematicidal Activity of the Volatilome of Eruca sativa on Meloidogyne incognita.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 6120-5, (2015) Research on new pesticides based on plant extracts, aimed at the development of nontoxic formulates, has recently gained increased interest. This study investigated the use of the volatilome of rucola (Eruca sativa) as a powerful natural nematicidal agent aga... |
|
|
Enhanced in vitro biological activity of synthetic 2-(2-pyridyl) ethyl isothiocyanate compared to natural 4-(methylsulfinyl) butyl isothiocyanate.
J. Med. Chem. 55(22) , 9682-92, (2012) Dietary isothiocyanates (ITC) derived from cruciferous vegetables have been shown to have numerous biological effects consistent with chemoprotective activity. In this study we synthesized a novel ITC, 2-(2-pyridyl) ethyl ITC (PY-ITC), and assessed its chemop... |
|
|
Metabolism of some naturally occurring isothiocyanates in the rat.
Xenobiotica 13(4) , 203-7, (1983) The metabolism of methyl, ethyl, butyl and allyl isothiocyanate, which occur as glucosinolates in a number of plants, was studied. Oral administration of the substances to the rat was followed by their renal excretion as mercapturic acids, which were isolated... |
|
|
Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of novel α- and β-dialkoxyphosphoryl isothiocyanates.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21 , 4572-4576, (2011) A series of 15 mostly new dialkoxyphosphoryl alkyl and aralkyl isothiocyanates were synthesized using two alternative strategies, and their in vitro antiproliferative activity against several cancer cell lines (including drug resistant) is here demonstrated. ... |
|
|
Monolayer-functionalized microfluidics devices for optical sensing of acidity.
Lab Chip 5(2) , 163-70, (2005) This paper describes the integration of opto-chemosensors in microfluidics networks. Our technique exploits the internal surface of the network as a platform to build a sensing system by coating the surface with a self-assembled monolayer and subsequently bin... |
|
|
Allyl-, butyl- and phenylethyl-isothiocyanate activate Nrf2 in cultured fibroblasts.
Pharmacol. Res. 63(3) , 233-40, (2011) The isothiocyanate sulforaphane (SFN) has been shown to induce phase 2 and antioxidant enzymes in cultured cells and in vivo via a Nrf2 dependent signal transduction pathway. However, little is known regarding the effect of structurally related compounds such... |
|
|
Semiquantitative analysis of 3-butenyl isothiocyanate to monitor an off-flavor in mustard seeds and glycosinolates screening for origin identification.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 58(6) , 3700-7, (2010) The present paper describes the development of an analytical method for the semiquantitative analysis of 3-butenyl isothiocyanate in mustard seeds, this compound being linked to an undesirable (at least for the European palate) off-flavor. 3-Butenyl isothiocy... |
|
|
Spectral studies of tert-butyl isothiocyanate-inactivated P450 2E1.
Biochemistry 40(24) , 7253-61, (2001) Inactivation of cytochrome P450 2E1 by tert-butyl isothiocyanate (tBITC) resulted in a loss in the spectrally detectable P450-reduced CO complex. The heme prosthetic group does not appear to become modified, since little loss of the heme was observed in the a... |
|
|
First investigation of the flavour profiles of the leaf, ripe fruit and root of Capparis spinosa var. mucronifolia from Iran. Afsharypuor S, et al.
Pharm. Acta Helv. 72(5) , 307-9, (1998)
|