Polyoxyethylene stearate
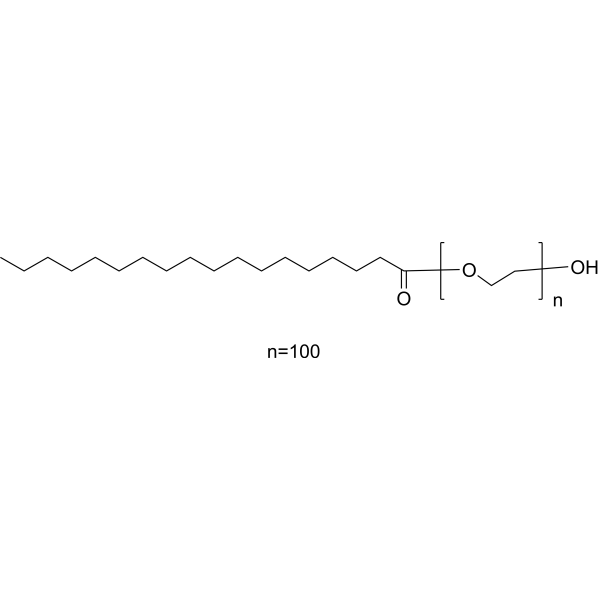
Polyoxyethylene stearate structure
|
Common Name | Polyoxyethylene stearate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9004-99-3 | Molecular Weight | 328.530 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 438.4±18.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H40O3 | Melting Point | 47ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 164.6±14.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
In Vivo Transfection and Detection of Gene Expression of Stem Cells Preloaded with DNA-carrying Microbubbles.
Radiology 276 , 518-25, (2015) To determine whether (a) stem cells loaded with DNA-carrying microbubbles (MBs) can be transfected in vivo, (b) the cells remain alive to express the gene, and (c) gene expression is sufficiently robust to be detected in vivo.The study was approved by the Ins... |
|
|
Enhanced bioavailability of sirolimus via preparation of solid dispersion nanoparticles using a supercritical antisolvent process.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 6 , 2997-3009, (2011) The aim of this study was to improve the physicochemical properties and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble sirolimus via preparation of a solid dispersion of nanoparticles using a supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process.First, excipients for enhancing th... |
|
|
[9-nitrocamptothecin nanostructured lipid carrier system: in vitro releasing characteristics, uptake by cells, and tissue distribution in vivo].
Yao Xue Xue Bao 40(11) , 970-5, (2005) To study the release and cell uptake characteristics of 9-nitrocamptothecin (9-NC) nanostructured lipid carrier system (NLC) in vitro and its tissue distribution characteristics in vivo.Mouse peritoneal macrophages were used to investigate the uptake of nanop... |
|
|
Non-linear response and viscoelastic properties of lipid-coated microbubbles: DSPC versus DPPC.
Ultrasound Med. Biol. 41(5) , 1432-45, (2015) For successful in vivo contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging (CEUS) and ultrasound molecular imaging, detailed knowledge of stability and acoustical properties of the microbubbles is essential. Here, we compare these aspects of lipid-coated microbubbles that h... |
|
|
In vivo and in vitro evaluations of water-absorption properties of various ointments.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 24(1) , 51-6, (1998) The water-absorption properties of various vehicles were evaluated in rats whose stratum corneum had been stripped off over the application site. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) applied to the site effectively absorbed the exudate, but other applied ointments absor... |
|
|
Action of Humicola lanuginosa lipase on mixed monomolecular films of tricaprylin and polyethylene glycol stearate.
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 63(1) , 91-100, (2008) The hydrolysis catalyzed by Humicola lanuginosa lipase (HLL) of pure tricaprylin (TC) or stearate of polyethylene glycol 1500 (PEG-St) as well as their mixtures spread as monomolecular films were studied. The catalytic transformation of the two substrates TC ... |
|
|
[Allergic respiratory disorders and vein sclerosis with lauromacrogol 400].
Therapie. 59(6) , 651-3, (2004)
|
|
|
Controlling lipolysis through steric surfactants: new insights on the controlled degradation of submicron emulsions after oral and intravenous administration.
Int. J. Pharm. 423(2) , 161-6, (2012) In this work we have investigated how steric surfactants influence the metabolic degradation of emulsions (lipolysis). To do so, we have prepared submicron emulsions stabilized with Pluronic F68, Pluronic F127, Myrj 52 or Myrj 59, four non-ionic surfactants w... |
|
|
Preparation and characteristics of nanostructured lipid carriers for control-releasing progesterone by melt-emulsification.
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 60(2) , 174-9, (2007) Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) made from mixtures of solid and spatially incompatible liquid lipids were prepared by melt-emulsification. Their drug loading capacity and releasing properties of progesterone were compared with those of solid lipid nanopar... |
|
|
Oral apomorphine delivery from solid lipid nanoparticles with different monostearate emulsifiers: pharmacokinetic and behavioral evaluations.
J. Pharm. Sci. 100(2) , 547-57, (2011) Apomorphine, a dopamine receptor agonist for treating Parkinson's disease, has very poor oral bioavailability (<2%) due to the first-pass effect. The aim of this work was to investigate whether the oral bioavailability and brain regional distribution of apomo... |