Chromium(III) chloride
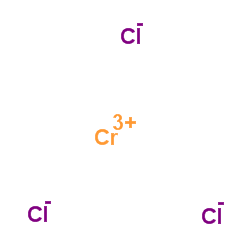
Chromium(III) chloride structure
|
Common Name | Chromium(III) chloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 10025-73-7 | Molecular Weight | 158.355 | |
| Density | 2.76 | Boiling Point | 1300°C | |
| Molecular Formula | Cl3Cr | Melting Point | 1152ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Genotoxicity of tri- and hexavalent chromium compounds in vivo and their modes of action on DNA damage in vitro.
PLoS ONE 9(8) , e103194, (2014) Chromium occurs mostly in tri- and hexavalent states in the environment. Hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] compounds are extensively used in diverse industries, and trivalent chromium [Cr(III)] salts are used as micronutrients and dietary supplements. In the prese... |
|
|
Tris(2-aminoethyl) amine functionalized silica gel for solid-phase extraction and preconcentration of Cr(III), Cd(II) and Pb(II) from waters.
J. Hazard. Mater. 157(1) , 154-60, (2008) A new tris(2-aminoethyl) amine (TREN) functionalized silica gel (SG-TREN) was prepared and investigated for selective solid-phase extraction (SPE) of trace Cr(III), Cd(II) and Pb(II) prior to its determination by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spe... |
|
|
Genotoxicity of trivalent chromium in bacterial cells. Possible effects on DNA topology.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 15(7) , 943-9, (2002) Trivalent chromium is a metal required for proper sugar and fat metabolism. However, it has been suggested that it causes DNA damage in in vitro test systems, although in vivo toxicity has not yet been proved. In the present study, the effect of Cr3+ on bacte... |
|
|
Differential impact of ionic and coordinate covalent chromium (Cr)-DNA binding on DNA replication.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 279(1-2) , 149-55, (2005) The reactive species produced by the reduction of Cr(VI), particularly Cr(III), can form both ionic and coordinate covalent complexes with DNA. These Cr(III)-DNA interactions consist of Cr-DNA monoadducts, Cr-DNA ternary adducts, and Cr-DNA interstrand cross-... |
|
|
Mobilization of trivalent chromium in presence of organic acids: a hydroponic study of wheat plant (Triticum vulgare).
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 63(4) , 524-30, (1999)
|
|
|
Bond distances are not always what they appear to be: discovery and un-discovery of the longest Cr(v)[triple bond, length as m-dash]N triple bond.
Dalton Trans. (14) , 1864-71, (2008) The coordination chemistry of CrCl3 with three pentadentate ligands having the [1,4,7]-triazacyclononane-1,4-diacetato motif have been investigated. The new resulting six-coordinate Cr(iii)-chloro species react cleanly with sodium azide to form the correspond... |
|
|
Chromium infusion in hospitalized patients with severe insulin resistance: a retrospective analysis.
Endocr. Pract. 18(3) , 394-8, (2012) To investigate the effects of intravenous chromium on serum glucose and insulin infusion rates in hospitalized patients with severe insulin resistance.In this retrospective study, we reviewed hospital records from January 1, 2008, to December 1, 2008, to iden... |
|
|
Improved glucose control associated with i.v. chromium administration in two patients receiving enteral nutrition.
Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 67(7) , 535-41, (2010) The effect of i.v. chromium administration on glucose control in two patients receiving enteral nutrition is described.Chromium supplementation has been hypothesized to potentiate the actions of insulin in facilitating cellular uptake of glucose. We report tw... |
|
|
Chromium improves glucose uptake and metabolism through upregulating the mRNA levels of IR, GLUT4, GS, and UCP3 in skeletal muscle cells.
Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 131(2) , 133-42, (2009) The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of three different chromium forms as chromic chloride (CrCl), chromium picolinate (CrPic), and a newly synthesized complex of chromium chelated with small peptides (CrSP) on glucose uptake and metabolism in vit... |
|
|
Nucleotide excision repair functions in the removal of chromium-induced DNA damage in mammalian cells.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 279(1-2) , 85-95, (2005) Some hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI))-containing compounds are human lung carcinogens. While ample information is available on the genetic lesions produced by Cr, surprisingly little is known regarding the cellular mechanisms involved in the removal of Cr-DNA add... |