PENITREM A
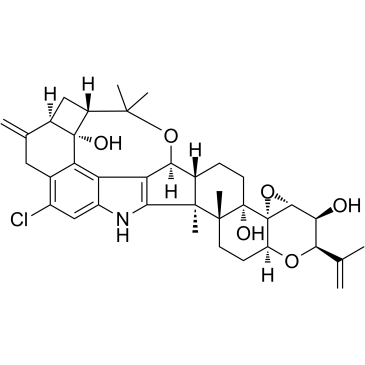
PENITREM A structure
|
Common Name | PENITREM A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 12627-35-9 | Molecular Weight | 634.201 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C37H44ClNO6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
5-hydroxytryptamine has an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-like effect on coronary flow in isolated rat hearts.
J. Biomed. Sci. 22 , 42, (2015) 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)-induced coronary artery responses have both vasoconstriction and vasorelaxation components. The vasoconstrictive effects of 5-HT have been well studied while the mechanism(s) of how 5-HT causes relaxation of coronary arteries has be... |
|
|
Small molecule regulators of autophagy identified by an image-based high-throughput screen.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104 , 19023-8, (2007) Autophagy is a lysosome-dependent cellular catabolic mechanism mediating the turnover of intracellular organelles and long-lived proteins. Reduction of autophagy activity has been shown to lead to the accumulation of misfolded proteins in neurons and may be i... |
|
|
Mechanisms underlying activation of transient BK current in rabbit urethral smooth muscle cells and its modulation by IP3-generating agonists.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 305(6) , C609-22, (2013) We used the perforated patch-clamp technique at 37°C to investigate the mechanisms underlying the activation of a transient large-conductance K(+) (tBK) current in rabbit urethral smooth muscle cells. The tBK current required an elevation of intracellular Ca(... |
|
|
LC-MS/MS screen for penitrem A and roquefortine C in serum and urine samples.
Anal. Chem. 78(13) , 4624-9, (2006) A rapid LC-MS/MS method, using a triple quadrupole/linear ion trap mass spectrometer, was developed for determination of penitrem A and roquefortine C in serum and urine samples. Penitrem A and roquefortine C were extracted from samples with methylene chlorid... |
|
|
Using roquefortine C as a biomarker for penitrem A intoxication.
J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 21(2) , 237-9, (2009) Penitrem A is a well-recognized tremorgenic mycotoxin produced by several Penicillium spp. However, most natural cases of penitrem A intoxication have been associated with Penicillium crustosum. Another Penicillium sp., Penicillium roqueforti, is used for the... |
|
|
Penitrem and thomitrem formation by Penicillium crustosum.
Mycopathologia 157(3) , 349-57, (2004) The levels of penitrems A, B, C, D, E, F, roquefortine C and thomitrem A and E recovered from extracts of 36 Norwegian, 2 American and one each of Japanese, German, South African, Danish and Fijian isolates of Penicillum crustosum Thom were quantitatively det... |
|
|
Comparison of secondary metabolite production by Penicillium crustosum strains, isolated from Arctic and other various ecological niches.
FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 53(1) , 51-60, (2005) Penicillium crustosum is common in food and feed both in subtropical and temperate regions. Recently, it has also been found occurring frequently in glacier ice, sea ice and sea water of Arctic regions of Svalbard. The aim of the study was to compare isolates... |
|
|
Poisoning of dogs with tremorgenic Penicillium toxins.
Med. Mycol 48(1) , 188-96, (2010) Fungi in the genus Penicillium, particularly P. crustosum, produce tremorgenic mycotoxins, as well as suspected tremorgenic compounds. The accidental intoxication of six dogs with such toxins are reported. The clinical signs included vomiting, convulsions, tr... |
|
|
Isolation and metabolite production by Penicillium roqueforti, P. paneum and P. crustosum isolated in Canada.
Mycopathologia 159(4) , 571-7, (2005) Penicillium roqueforti, P. crustosum and P. paneum grow on ensiled grain and recycled feed unless properly treated. The former two species occur also on cut lumber in Canada. These are known to produce a number of secondary metabolites including roquefortine.... |
|
|
Impaired function of coronary BK(Ca) channels in metabolic syndrome.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 297(5) , H1629-37, (2009) The role of large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK(Ca)) channels in regulation of coronary microvascular function is widely appreciated, but molecular and functional changes underlying the deleterious influence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) have not been ... |