Remacemide hydrochloride
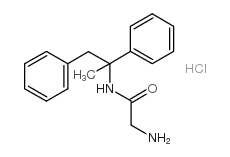
Remacemide hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Remacemide hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 111686-79-4 | Molecular Weight | 304.81400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 466.4ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H21ClN2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 235.9ºC | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
The cognitive and psychomotor effects of remacemide and carbamazepine in newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Epilepsy Behav. 14(3) , 522-8, (2009) An international trial comparing remacemide hydrochloride with carbamazepine was undertaken in individuals with newly diagnosed epilepsy using a novel double-blind, parallel-group, double triangular sequential design. Patients with two or more partial or gene... |
|
|
Chronic exposure to NMDA receptor and sodium channel blockers during development in monkeys and rats: long-term effects on cognitive function.
Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 993 , 116-22; discussion 123-4, (2003) The effects of chronic administration of MK-801 (NMDA-receptor antagonist) and remacemide (sodium channel blocker) on monkey learning of several brain function tasks was assessed in juveniles (nine months old). Low (LO) and high (HI) doses of both drugs were ... |
|
|
Coenzyme Q10 and remacemide hydrochloride ameliorate motor deficits in a Huntington's disease transgenic mouse model.
Neurosci. Lett. 315(3) , 149-53, (2001) Huntington's disease (HD) is a progressive inherited neurodegenerative disorder, for which there is no effective therapy. The CARE-HD study, recently published, evaluated the ability of a combination of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and remacemide hydrochloride (R) to... |
|
|
Lamotrigine and remacemide protect striatal neurons against in vitro ischemia: an electrophysiological study.
Exp. Neurol. 182(2) , 461-9, (2003) In the present study, we investigated the cellular and synaptic mechanisms underlying the neuroprotective action of lamotrigine and remacemide. Both drugs, in fact, have been reported to exert a neuroprotective action in in vivo animal models of ischemia. To ... |
|
|
Assessing the potential toxicity of MK-801 and remacemide::Chronic exposure in juvenile rhesus monkeys
Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 24(2) , 193-207, (2002) The present experiment examined the effects of chronic exposure to either 0.1 or 1.0 mg/kg MK-801 [a selective N-methyl- d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist] or 20.0 or 50.0 mg/kg remacemide (an NMDA receptor antagonist which also blocks fast sodium channe... |
|
|
Behavioral effects associated with chronic ketamine or remacemide exposure in rats.
Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 29(3) , 348-59, (2007) The effects of chronic exposure to ketamine or remacemide on the acquisition and performance of food-reinforced operant behaviors was assessed in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Ketamine is an anesthetic N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, whereas re... |
|
|
Effects of manipulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on imipenem/cilastatin-induced seizures in rats.
Indian J. Med. Res. 119(2) , 79-85, (2004) Epileptic seizures have been reported in patients on imipenem/cilastatin (Imi/Cil) therapy. To investigate contribution of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in inducing imipenem/cilastatin (Imi/Cil) seizures, the effects of competitive NMDA antagonist, AP... |
|
|
A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of remacemide hydrochloride in patients with refractory epilepsy following pre-surgical assessment.
Seizure 11(6) , 371-6, (2002) This multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study investigated the efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of remacemide hydrochloride in adult patients ( n= 59) with refractory epilepsy, undergoing reduced or discontinued ant... |
|
|
Influence of cytochrome P450 induction on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of remacemide hydrochloride.
Epilepsy Res. 49(3) , 247-54, (2002) Remacemide hydrochloride (RMD) is a putative anticonvulsant agent with an active metabolite, desglycinyl-remacemide (DGR) and a broad spectrum of activity in experimental seizure models. In clinical trials, however, the efficacy of RMD is questionable. In the... |
|
|
Isobolographic analysis of interactions between remacemide and conventional antiepileptic drugs in the mouse model of maximal electroshock.
Epilepsy Behav. 11(1) , 6-12, (2007) Using the mouse maximal electroshock-induced seizure model, indicative of tonic-clonic seizures in humans, the present study was aimed at characterizing the interaction between remacemide and valproate, carbamazepine, phenytoin, and phenobarbital. Isobolograp... |