berythromycin
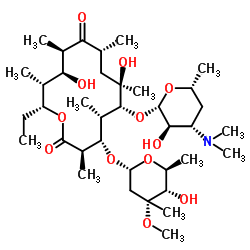
berythromycin structure
|
Common Name | berythromycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 527-75-3 | Molecular Weight | 717.927 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 807.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C37H67NO12 | Melting Point | 168-170ºC (dec) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 442.2±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
A simple and rapid confirmatory assay for analyzing antibiotic residues of the macrolide class and lincomycin in bovine milk and yoghurt: hot water extraction followed by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 21(2) , 237-46, (2007) A rapid and simple sample preparation procedure for determining residues of antibiotics of the class of macrolides and lincomycin in whole milk and yoghurt by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) is presented. The method is based on the m... |
|
|
Acid-catalyzed degradation of clarithromycin and erythromycin B: a comparative study using NMR spectroscopy.
J. Med. Chem. 43(3) , 467-74, (2000) One of the major drawbacks in the use of the antibiotic erythromycin A is its extreme acid sensitivity, leading to degradation in the stomach following oral administration. The modern derivative clarithromycin degrades by a different mechanism and much more s... |
|
|
An abiotic strategy for the enantioselective synthesis of erythromycin B.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 42(28) , 3278-81, (2003)
|
|
|
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of stable and taste-free erythromycin proprodrugs.
J. Med. Chem. 48(11) , 3878-84, (2005) Erythromycin A is normally formulated for children as its 2'-ethyl succinate, a taste-free prodrug. Unfortunately, the prodrug hydrolyzes at a measurable rate in the medicine bottle, leading to the vile-tasting erythromycin. We have prepared derivatives of er... |
|
|
An unexpected interaction between the modular polyketide synthases, erythromycin DEBS1 and pikromycin PikAIV, leads to efficient triketide lactone synthesis.
Biochemistry 41(35) , 10827-33, (2002) An unusual feature of the 6-module pikromycin polyketide synthase (PikPKS, PikAI-PikAIV) of S. venezuelae is the ability to generate both 12- and 14-membered ring macrolides. The PikAIV component containing the last extension module and a thioesterase domain ... |
|
|
Chemical modification of erythromycins. IV. Synthesis and biological properties of 6-O-methylerythromycin B.
J. Antibiot. 43(5) , 544-9, (1990) 6-O-Methylerythromycin B has been synthesized from erythromycin B via regioselective methylation of the 6-hydroxyl group in 71% overall yield. This compound shows in vitro antibacterial activity comparable to erythromycins A and B and exhibits superior in viv... |
|
|
Production of 6-deoxy-13-cyclopropyl-erythromycin B by Saccharopolyspora erythraea NRRL 18643.
J. Antibiot. 52(8) , 742-7, (1999) Cyclopropane carboxylic acid was fed to Saccharopolyspora erythraea NRRL 18643 (6-deoxyerythromycin producer), resulting in the production of 6-deoxy-13-cyclopropyl-erythromycin B. These studies provide further evidence that deoxyerythronolide B synthase has ... |
|
|
Knocking out of tailoring genes eryK and eryG in an industrial erythromycin-producing strain of Saccharopolyspora erythraea leading to overproduction of erythromycin B, C and D at different conversion ratios.
Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 52(2) , 129-37, (2011) To overproduce erythromycin C, B or D and evaluate the effect of disruption of tailoring genes eryK and eryG in an industrial erythromycin producer. The tailoring genes eryG and eryK were inactivated individually or simultaneously by targeted gene disruptio... |