GW9508
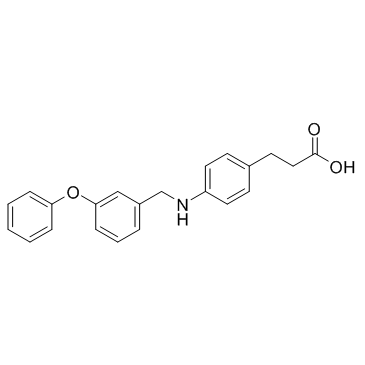
GW9508 structure
|
Common Name | GW9508 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 885101-89-3 | Molecular Weight | 347.407 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 538.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H21NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 279.4±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Omega-3 fatty acids and other FFA4 agonists inhibit growth factor signaling in human prostate cancer cells.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 352(2) , 380-94, (2015) Omega-3 fatty acids (n-3 FAs) are proposed to have many beneficial effects on human health. However, the mechanisms underlying their potential cancer preventative effects are unclear. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) of the free fatty acid receptor (FFAR) ... |
|
|
Short-chain fatty acid sensing in rat duodenum.
J. Physiol. 593(3) , 585-99, (2015) Luminal lipid in the duodenum modulates gastroduodenal functions via the release of gut hormones and mediators such as cholecystokinin and 5-HT. The effects of luminal short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the foregut are unknown. Free fatty acid receptors (FFAR... |
|
|
Novel identification of the free fatty acid receptor FFAR1 that promotes contraction in airway smooth muscle.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 309 , L970-82, (2015) Obesity is one of the major risk factors for asthma. Previous studies have demonstrated that free fatty acid levels are elevated in the plasma of obese individuals. Medium- and long-chain free fatty acids act as endogenous ligands for the free fatty acid rece... |
|
|
Mercaptoacetate and fatty acids exert direct and antagonistic effects on nodose neurons via GPR40 fatty acid receptors.
Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 307(1) , R35-43, (2014) β-mercaptoacetate (MA) is a drug known to block mitochondrial oxidation of medium- and long-chain fatty acids (FAs) and to stimulate feeding. Because MA-induced feeding is vagally dependent, it has been assumed that the feeding response is mediated by MA's an... |
|
|
Proinflammatory effects of arachidonic acid in a lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory microenvironment in 3T3-L1 adipocytes in vitro.
Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 40(2) , 142-54, (2015) Long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5n-3, EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3, DHA), have known anti-inflammatory effects, including the modulation of adipose tissue-derived inflammatory mediators (i.e., adipokines)... |
|
|
Evidence for the involvement of GPR40 and NADPH oxidase in palmitic acid-induced superoxide production and insulin secretion.
Islets 5(4) , 139-48, (2013) G protein coupled receptor 40 (GPR40) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase complex have been shown to be involved in the fatty acid amplification of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). The effect of palmitic acid on superox... |
|
|
GW9508, a free fatty acid receptor agonist, specifically induces cell death in bone resorbing precursor cells through increased oxidative stress from mitochondrial origin.
Exp. Cell Res. 319(19) , 3035-41, (2013) GW9508 is a free fatty acid receptor agonist able to protect from ovariectomy-induced bone loss in vivo thought inhibition of osteoclast differentiation in a G-coupled Protein Receptor 40 (GPR40)-dependent way. In this study, we questioned whether higher dose... |
|
|
A novel anti-inflammatory role of GPR120 in intestinal epithelial cells.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 310 , C612-21, (2016) GPR120 (free fatty acid receptor-4) is a G protein-coupled receptor for medium- and long-chain unsaturated fatty acids, including ω-3 fatty acids. Recent studies have shown GPR120 to play cardinal roles in metabolic disorders via modulation of gut hormone sec... |
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits inflammation via free fatty acid receptor FFA4, disruption of TAB2 interaction with TAK1/TAB1 and downregulation of ERK-dependent Egr-1 expression in EA.hy926 cells.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 60 , 430-43, (2016) Inflammation is intimately associated with many cardiovascular events and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) has been shown to protect against CVD. Egr-1 has emerged as a key regulator in the development of atherosclerosis. Free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4) is an n-3... |
|
|
Linoleic acid stimulates [Ca2+]i increase in rat pancreatic beta-cells through both membrane receptor- and intracellular metabolite-mediated pathways.
PLoS ONE 8 , e60255, (2013) The role of the free fatty acid (FFA) receptor and the intracellular metabolites of linoleic acid (LA) in LA-stimulated increase in cytosolic free calcium concentration ([Ca(2+)]i) was investigated. [Ca(2+)]i was measured using Fura-2 as indicator in rat panc... |