4-tert-Butylcatechol
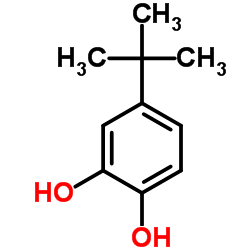
4-tert-Butylcatechol structure
|
Common Name | 4-tert-Butylcatechol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 98-29-3 | Molecular Weight | 166.217 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 286.3±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H14O2 | Melting Point | 52-55 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 135.5±16.4 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Preparation and evaluation of monolithic poly(N-vinylcarbazole-co-1,4-divinylbenzene) capillary columns for the separation of small molecules.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem , (2014) Short-term polymerization or the so-called low-conversion polymerization was applied for the preparation of N-vinylcarbazole (NVC) and 1,4-divinylbenzene (DVB) monolithic capillary columns. The synthesis was carried out by thermally initiated free radical cop... |
|
|
A simple approach for ultrasensitive detection of bisphenols by multiplexed surface-enhanced Raman scattering.
Anal. Chim. Acta 888 , 118-25, (2015) Bisphenol A (BPA) is well known for its use in plastic manufacture and thermal paper production despite its risk of health toxicity as an endocrine disruptor in humans. Since the publication of new legislation regarding the use of BPA, manufacturers have begu... |
|
|
The pro-enzyme C-terminal processing domain of Pholiota nameko tyrosinase is responsible for folding of the N-terminal catalytic domain.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 , 5499-510, (2015) Pholiota nameko (Pholiota microspore) tyrosinase is expressed as a latent 67-kDa pro-tyrosinase, comprising a 42-kDa N-terminal catalytic domain with a binuclear copper centre and a 25-kDa C-terminal domain and is activated by proteolytic digestion of the C-t... |
|
|
Reduction in eumelanin by the activation of glutathione reductase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase after exposure to a depigmenting chemical.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 32(8) , 1379-82, (1983) Topical application of 4-tertiary butyl catechol (TBC) causes vitiligo in the skin of man and animals, and previous electron microscopic studies showed pheomelanin formation in the affected areas. In the present study, we investigated changes of enzyme activi... |
|
|
Screen-printed immunosensor modified with carbon nanotubes in a continuous-flow system for the Botrytis cinerea determination in apple tissues.
Talanta 79(3) , 681-6, (2009) Botrytis cinerea is a plant-pathogenic fungus that produces the disease known as grey mould in a wide variety of agriculturally important hosts in many countries. This paper describes the development of an immunosensor coupled to carbon-based screen-printed e... |
|
|
Occupational dermatoses among fibreglass-reinforced plastics factory workers.
Contact Dermatitis 46(6) , 339-47, (2002) Fibreglass-reinforced plastics (FRP) factory workers are at high risk of developing occupational dermatoses because of their exposure to many chemicals used in the manufacture of plastics as well as to glass fibre or dust. Patch tests were carried out on 29 w... |
|
|
An unusual delayed patch test reaction to para-tertiary-butylcatechol.
Contact Dermatitis 22(2) , 110-1, (1990)
|
|
|
Effects of 4-tertiary butyl catechol on glutathione-metabolizing enzymes in vivo and in vitro.
J. Invest. Dermatol. 82(1) , 53-6, (1984) 4-Tertiary butyl catechol (TBC) causes depigmentation in humans and animals and stimulates formation of pheomelanosomes. In this study, we investigated the effects of noncytotoxic doses of TBC on glutathione S-transferase (GST) activity in the skin of Uscd st... |
|
|
Contact sensitivity to para-tertiary-butylcatechol in an artificial limb.
Contact Dermatitis 22(1) , 56-7, (1990)
|
|
|
Occupational vitiligo and contact sensitivity to para-tertiary butyl catechol.
Contact Dermatitis 25(3) , 200-1, (1991)
|