Betaine
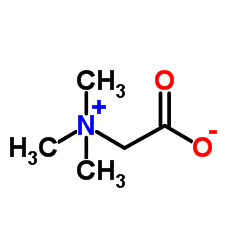
Betaine structure
|
Common Name | Betaine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 107-43-7 | Molecular Weight | 117.146 | |
| Density | 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2 | Melting Point | 301-305 °C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
The fused anthranilate synthase from Streptomyces venezuelae functions as a monomer.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 400(1-2) , 9-15, (2015) Recently, we showed that the fused chorismate-utilizing enzyme from the antibiotic-producing soil bacterium Streptomyces venezuelae is an anthranilate synthase (designated SvAS), not a 2-amino-2-deoxyisochorismate (ADIC) synthase, as was predicted based on it... |
|
|
Rectification of impaired adipose tissue methylation status and lipolytic response contributes to hepatoprotective effect of betaine in a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 171(17) , 4073-86, (2014) Overactive lipolysis in adipose tissue contributes to the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease (ALD); however, the mechanisms involved have not been elucidated. We previously reported that chronic alcohol consumption produces a hypomethylation state in adi... |
|
|
Generation and characterization of a murine model of Bietti crystalline dystrophy.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(9) , 5572-81, (2014) Bietti crystalline dystrophy (BCD) is a rare, autosomal recessive, progressive, degenerative eye disease caused by mutations in the CYP4V2 gene, for which no treatments are currently available. Cyp4v3 is the murine ortholog to CYP4V2, and to better understand... |
|
|
Simultaneous Identification of Potential Pathogenicity Factors of Mycoplasma agalactiae in the Natural Ovine Host by Negative Selection.
Infect. Immun. 83 , 2751-61, (2015) Mycoplasmas possess complex pathogenicity determinants that are largely unknown at the molecular level. Mycoplasma agalactiae serves as a useful model to study the molecular basis of mycoplasma pathogenicity. The generation and in vivo screening of a transpos... |
|
|
LAMP technology: Rapid identification of Brucella and Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis.
Braz. J. Microbiol. 46 , 619-26, (2015) In this study, we developed new sets of primers to detect Brucella spp. and M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) through isothermal amplification. We selected a previously well-characterized target gene, bscp31, specific for Brucella spp. and IS900 for MAP.... |
|
|
HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome.
Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database issue) , D603-10, (2009) The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB, http://www.hmdb.ca) is a richly annotated resource that is designed to address the broad needs of biochemists, clinical chemists, physicians, medical geneticists, nutritionists and members of the metabolomics community. Si... |
|
|
The human serum metabolome.
PLoS ONE 6(2) , e16957, (2011) Continuing improvements in analytical technology along with an increased interest in performing comprehensive, quantitative metabolic profiling, is leading to increased interest pressures within the metabolomics community to develop centralized metabolite ref... |
|
|
Prediction of skeletal muscle and fat mass in patients with advanced cancer using a metabolomic approach.
J. Nutr. 142(1) , 14-21, (2012) Urine and plasma metabolites originate from endogenous metabolic pathways in different organs and exogenous sources (diet). Urine and plasma were obtained from advanced cancer patients and investigated to determine if variations in lean and fat mass, dietary ... |
|
|
Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression.
Nature 457(7231) , 910-4, (2009) Multiple, complex molecular events characterize cancer development and progression. Deciphering the molecular networks that distinguish organ-confined disease from metastatic disease may lead to the identification of critical biomarkers for cancer invasion an... |
|
|
Extreme urinary betaine losses in type 2 diabetes combined with bezafibrate treatment are associated with losses of dimethylglycine and choline but not with increased losses of other osmolytes.
Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 28(5) , 459-68, (2014) Betaine deficiency is a probable cardiovascular risk factor and a cause of elevated homocysteine. Urinary betaine excretion is increased by fibrate treatment, and is also often elevated in diabetes. Does fibrate further increase betaine excretion in diabetes,... |