3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
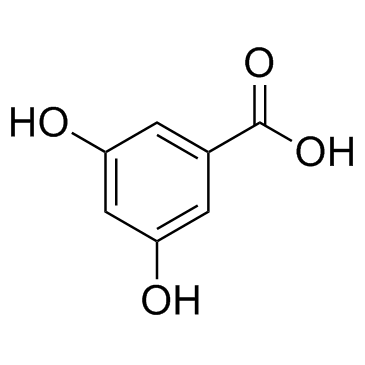
3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 99-10-5 | Molecular Weight | 154.120 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 411.5±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 | Melting Point | 236-238 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 216.8±16.9 °C | |
|
Click to a focused library of benzyl 6-triazolo(hydroxy)benzoic glucosides: novel construction of PTP1B inhibitors on a sugar scaffold.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46 , 4212-8, (2011) With an aim of developing novel protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) 1B inhibitors based on sugar scaffolds, a focused library of benzyl 6-triazolo(hydroxy)benzoic glucosides was efficiently constructed via the modular and selective Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne... |
|
|
Inhibition of 15-lipoxygenase-catalysed oxygenation of arachidonic acid by substituted benzoic acids.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 4589-93, (2008) Elevated levels of phospholipases, prostaglandin synthases and lipoxygenases in colonic cells at various stages of malignancy indicate a strong link between dietary lipids and colon cancer. Lipoxygenase-catalysed arachidonic acid metabolism plays a key role i... |
|
|
In vitro inhibition of α-carbonic anhydrase isozymes by some phenolic compounds.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21 , 4259-62, (2011) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) are a class of pharmaceuticals used as antiglaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, gastric and duodenal ulcers, neurological disorders or osteoporosis. We report here the inhibit... |
|
|
Convergent synthesis of 4,5-branched inner-core oligosaccharides of lipopoly- and lipooligosaccharides.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 79 , 1931-45, (2015) The convergent synthesis of branched inner-core oligosaccharides of lipopoly- and lipooligosaccharide with a 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid (Kdo) disaccharide acceptor was achieved. The l-glycero-d-manno-heptopyranose (Hep) units for the branched core ol... |
|
|
Improvement of pro-oxidant capacity of protocatechuic acid by esterification.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e110277, (2014) Pro-oxidant effects of phenolic compounds are usually correlated to the one-electron redox potential of the phenoxyl radicals. Here we demonstrated that, besides their oxidizability, hydrophobicity can also be a decisive factor. We found that esterification o... |
|
|
Mass spectrometric behavior of phenolic acids standards and their analysis in the plant samples with LC/ESI/MS system.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 967 , 21-7, (2014) Liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) with electrospray ionization (ESI) is one of analytical techniques to obtain accurate results of low molecular weight aromatic compounds in biological samples of different origin. The interpretations of ... |
|
|
Liquid chromatographic/electrospray ionization mass spectrometric identification of the oxidation end-products of trans-resveratrol in aqueous solutions.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 24(5) , 634-42, (2010) trans-Resveratrol (3,5,4'-trihydroxystilbene) is a natural polyphenolic compound that exhibits antioxidant properties. Our study aimed at studying the HO*-induced oxidation of resveratrol (100 micromol.L(-1)) in aerated aqueous solutions. Gamma radiolysis of ... |
|
|
Structural characteristics of green tea catechins for formation of protein carbonyl in human serum albumin.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 4892-6, (2010) Catechins are polyphenolic antioxidants found in green tea leaves. Recent studies have reported that various polyphenolic compounds, including catechins, cause protein carbonyl formation in proteins via their pro-oxidant actions. In this study, we evaluate th... |
|
|
Biphenyl 4-Hydroxylases Involved in Aucuparin Biosynthesis in Rowan and Apple Are Cytochrome P450 736A Proteins.
Plant Physiol. 168 , 428-42, (2015) Upon pathogen attack, fruit trees such as apple (Malus spp.) and pear (Pyrus spp.) accumulate biphenyl and dibenzofuran phytoalexins, with aucuparin as a major biphenyl compound. 4-Hydroxylation of the biphenyl scaffold, formed by biphenyl synthase (BIS), is ... |
|
|
Kinetic and docking studies of phenol-based inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase isoforms I, II, IX and XII evidence a new binding mode within the enzyme active site.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 1381-9, (2011) Carbonic anhydrases (CAs, EC 4.2.1.1) are inhibited by sulfonamides, inorganic anions, phenols, coumarins (acting as prodrugs) and polyamines. A novel class of CA inhibitors (CAIs), interacting with the CA isozymes I, II (cytosolic) and IX, XII (transmembrane... |