Piperazine
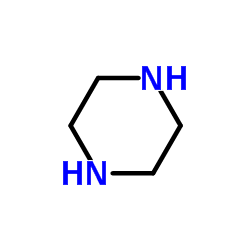
Piperazine structure
|
Common Name | Piperazine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 110-85-0 | Molecular Weight | 86.136 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 149.3±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10N2 | Melting Point | 109-112 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 49.7±10.2 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Polyoxometalates--potent and selective ecto-nucleotidase inhibitors.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 93(2) , 171-81, (2015) Polyoxometalates (POMs) are inorganic cluster metal complexes that possess versatile biological activities, including antibacterial, anticancer, antidiabetic, and antiviral effects. Their mechanisms of action at the molecular level are largely unknown. Howeve... |
|
|
Characterizing the structure of lipodisq nanoparticles for membrane protein spectroscopic studies.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1848(1 Pt B) , 329-33, (2015) Membrane protein spectroscopic studies are challenging due to the difficulty introduced in preparing homogenous and functional hydrophobic proteins incorporated into a lipid bilayer system. Traditional membrane mimics such as micelles or liposomes have proved... |
|
|
Mutations in intron 1 and intron 22 inversion negative haemophilia A patients from Western India.
PLoS ONE 9(5) , e97337, (2014) Despite increased awareness and diagnostic facilities, 70-80% of the haemophilia A (HA) patients still remain undiagnosed in India. Very little data is available on prevalent mutations in HA from this country. We report fifty mutations in seventy one Indian H... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Enhanced oral bioavailability of morin administered in mixed micelle formulation with PluronicF127 and Tween80 in rats.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38(2) , 208-17, (2015) To overcome the low oral bioavailability of morin, a mixed micelle formulation with pharmaceutical excipients that facilitate solubilization and modulate P-glycoprotein (P-gp) was developed and evaluated in vitro and in vivo rats. Morin-loaded mixed micelle f... |
|
|
Comparison of liquid chromatography and supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to compact single quadrupole mass spectrometer for targeted in vitro metabolism assay.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1371 , 244-56, (2014) The goal of this study was to evaluate the combination of powerful chromatographic methods and compact single quadrupole MS device for simple in vitro cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibition assay, instead of more expensive triple quadrupole MS/MS detectors. For thi... |
|
|
Controlling osteogenic stem cell differentiation via soft bioinspired hydrogels.
PLoS ONE 9(6) , e98640, (2014) Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) is guided by various physical and biochemical factors. Among these factors, modulus (i.e., rigidiy) of the ECM has gained significant attention as a physical osteoinductive signal that can con... |
|
|
Synthesis and antitumor activities of some new N1-(flavon-6-yl)amidrazone derivatives.
Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 347(6) , 415-22, (2014) A new series of N1-(flavon-6-yl)amidrazones were synthesized by reacting the hydrazonoyl chloride derived from 6-aminoflavone with the appropriate sec-cyclic amines. The antitumor activities of these compounds were evaluated on breast cancer (MCF-7) and leuke... |
|
|
Enthalpy contributions to adsorption of highly charged lysozyme onto a cation-exchanger under linear and overloaded conditions.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1352 , 46-54, (2014) An investigation of the adsorption mechanism of lysozyme onto carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) was conducted using flow calorimetry and adsorption isotherm measurements. This study was undertaken to provide additional insight into the underlying mechanisms invol... |
|
|
The seleno-organic compound ebselen impairs mitochondrial physiology and induces cell death in AR42J cells.
Toxicol. Lett. 229(3) , 465-73, (2014) Ebselen is a seleno-organic compound that causes cell death in several cancer cell types. The mechanisms underlying its deleterious effects have not been fully elucidated. In this study, the effects of ebselen (1 μM-40 μM) on AR42J tumor cells have been exami... |