Chlorimuron-ethyl
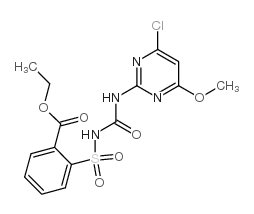
Chlorimuron-ethyl structure
|
Common Name | Chlorimuron-ethyl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90982-32-4 | Molecular Weight | 414.82100 | |
| Density | 1.493 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H15ClN4O6S | Melting Point | 180-182°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Response of multiple seeded cocklebur and other cocklebur types to herbicide treatment.
Pest Manag. Sci. 61(7) , 643-8, (2005) Multiple seeded cocklebur has been found in the last decade in Texas, and described as a biotype of Xanthium strumarium L with up to 25 seeds per bur instead of the usual two. The multiple seeded bur typically produces up to nine seedlings, causing concern th... |
|
|
Magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental water samples by Fe3O4@dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride@silica magnetic particles.
Anal. Chim. Acta 747 , 29-35, (2012) A magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) method coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was proposed for the determination of five sulfonylurea herbicides (bensulfuron-methyl, prosulfuron, pyrazosulfuron-ethyl, chlorimuron-ethyl and triflus... |
|
|
Elucidating the specificity of binding of sulfonylurea herbicides to acetohydroxyacid synthase.
Biochemistry 44(7) , 2330-8, (2005) Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS, EC 2.2.1.6) is the target for the sulfonylurea herbicides, which act as potent inhibitors of the enzyme. Chlorsulfuron (marketed as Glean) and sulfometuron methyl (marketed as Oust) are two commercially important members of th... |
|
|
Examination of the translocation of sulfonylurea herbicides in sunflower plants by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry imaging.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 24(22) , 3309-19, (2010) Pesticides are widely used in agriculture to control weeds, pests and diseases. Successful control is dependent on the compound reaching the target site within the organism after spray or soil application. Conventional methods for determining uptake and movem... |
|
|
Single and joint effects of pesticides and mercury on soil urease.
J. Environ. Sci. (China) 19(2) , 210-6, (2007) The influence of two pesticides including chlorimuron-ethyl and furadan and mercury (Hg) on urease activity in 4 soils (meadow burozem and phaeozem) was investigated. The soils were exposed to various concentrations of the two pesticides and Hg individually a... |
|
|
Ecological risk of long-term chlorimuron-ethyl application to soil microbial community: an in situ investigation in a continuously cropped soybean field in Northeast China.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 18(3) , 407-15, (2011) Chlorimuron-ethyl has been widely used for the soybean production of China, but less information is available on the possible risk of long-term application of this herbicide.In this paper, soil samples were collected from the plots having been received 30 g a... |
|
|
Biodegradation of the sulfonylurea herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl by the strain Pseudomonas sp. LW3.
FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 296(2) , 203-9, (2009) The chlorimuron-ethyl-degrading bacterium LW3 was isolated from contaminated soil and identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing as Pseudomonas sp. When chlorimuron-ethyl was provided as the sole nitrogen source, the degradation efficiency in liquid medium was ab... |
|
|
Toxicological responses in wheatTriticum aestivumunder joint stress of chlorimuron-ethyl and copper
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 72(8) , 2121-9, (2009) It was observed in this work that joint effects of chlorimuron-ethyl and copper on chlorophyll content, the peroxidases (POD) activity, superoxide dismutases (SOD) activity and soluble protein content in leaves and roots of wheat were markedly significant. Th... |
|
|
Isolation and characterization of Sporobolomyces sp. LF1 capable of degrading chlorimuron-ethyl.
J. Environ. Sci. (China) 21(9) , 1253-60, (2009) A yeast strain which was capable of degrading sulfonylurea herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl named as LF1 was isolated from a chlorimuron-ethyl contaminated soil near the warehouse of the factory producing chlorimuron-ethyl in Shenyang City, Northeast China. The st... |
|
|
Biodegradation of chlorimuron-ethyl by the bacterium Klebsiella jilinsis 2N3.
J. Environ. Sci. Health B 45(6) , 501-7, (2010) Enrichment culturing of sludge taken from an industrial wastewater treatment pond led to the identification of a bacterium (Klebsiella jilinsis H. Zhang) that degrades chlorimuron-ethyl with high efficiency. Klebsiella jilinsis strain 2N3 grows with chlorimur... |