Bromochloroacetic Acid
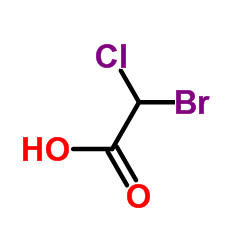
Bromochloroacetic Acid structure
|
Common Name | Bromochloroacetic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5589-96-8 | Molecular Weight | 173.393 | |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 214.8±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H2BrClO2 | Melting Point | 27.5ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 83.7±21.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Mammalian cell cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of the haloacetic acids, a major class of drinking water disinfection by-products.
Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 51(8-9) , 871-8, (2010) The haloacetic acids (HAAs) are disinfection by-products (DBPs) that are formed during the disinfection of drinking water, wastewaters and recreational pool waters. Currently, five HAAs [bromoacetic acid (BAA), dibromoacetic acid (DBAA), chloroacetic acid (CA... |
|
|
Chemical and bioanalytical assessments on drinking water treatments by quaternized magnetic microspheres.
J. Hazard. Mater. 285 , 53-60, (2015) This study aimed to compare the toxicity reduction performance of conventional drinking water treatment (CT) and a treatment (NT) with quaternized magnetic microspheres (NDMP) based on chemical analyses. Fluorescence excitation-emission-matrix combined with p... |
|
|
Mouse embryonic stem cell adherent cell differentiation and cytotoxicity (ACDC) assay.
Reprod. Toxicol. 31(4) , 383-91, (2011) An adherent cell differentiation and cytotoxicity (ACDC) assay was developed using pluripotent J1 mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs). Adherent mESCs were used to evaluate chemical-induced effects on both stem cell viability and differentiation using an in-cel... |
|
|
Reproductive and genomic effects in testes from mice exposed to the water disinfectant byproduct bromochloroacetic acid.
Reprod. Toxicol. 19(3) , 353-66, (2005) A byproduct of drinking water disinfection, bromochloroacetic acid (BCA), acts as a reproductive toxicant in rats. To determine if BCA produces similar reproductive toxicity in mice, juvenile and adult C57BL/6 males were exposed to 0, 8, 24, 72 or 216 mg/kg o... |
|
|
Bromochloro-haloacetic acids: effects on mouse embryos in vitro and QSAR considerations.
Reprod. Toxicol. 21(3) , 260-6, (2006) The haloacetic acids (HAA) are a family of chemicals that are drinking water disinfection by-products. We previously reported that haloacetic acids, including several bromo- and chloro-HAAs, alter embryonic development when mouse conceptuses are directly expo... |
|
|
Use of structure-activity relationships for probing biochemical mechanisms: glutathione transferase zeta conjugation of haloacids.
Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 500 , 23-31, (2001)
|
|
|
The disinfection by-products dichloro-, dibromo-, and bromochloroacetic acid impact intestinal microflora and metabolism in Fischer 344 rats upon exposure in drinking water.
Toxicol. Sci. 56(2) , 282-9, (2000) Human consumption of chlorinated drinking water has been linked epidemiologically to bladder, kidney, and rectal cancers. The disinfection by-product (DBP) dichloroacetic acid is a hepatocarcinogen in Fischer 344 rats and B6C3F1 mice. The objective of this st... |
|
|
Short-term exposures to dihaloacetic acids produce dysmorphogenesis in mouse conceptuses in vitro.
Reprod. Toxicol. 22(3) , 443-8, (2006) The haloacetic acids (HAAs) are a family of xenobiotics found in tap water as a result of drinking water disinfection. Administration of HAAs to rats produces a variety of adverse effects, including developmental toxicity. The dysmorphogenic potencies of all ... |
|
|
Evaluation of the effects of water disinfection by-products, bromochloroacetic and dibromoacetic acids, on frog embryogenesis.
J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 67(12) , 929-39, (2004) Adverse developmental effects of two haloacetic acids, bromochloroacetic acid (BCA) and dibromoacetic acid (DBA), were determined by using the Frog Embryo Teratogenesis Assay--Xenopus (FETAX). Xenopus embryos (150-400/concentration group) were exposed to 0, 8... |
|
|
Development of normal human colon cell cultures to identify priority unregulated disinfection by-products with a carcinogenic potential.
Water Sci. Technol. 56(12) , 51-5, (2007) Research was initiated to develop an in vitro system to identify disinfection by-products with a potential to transform normal human colonocytes into malignant cells. Tribromomethane and bromochloroacetic acid, rodent colon carcinogens, dibromonitromethane an... |