1,4-Dianilinobenzene
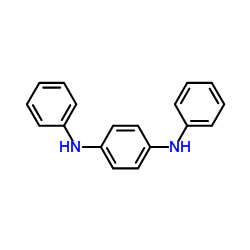
1,4-Dianilinobenzene structure
|
Common Name | 1,4-Dianilinobenzene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 74-31-7 | Molecular Weight | 260.333 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 469.2±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H16N2 | Melting Point | 143-145 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 297.0±13.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Skin sensitization potency and cross-reactivity of p-phenylenediamine and its derivatives evaluated by non-radioactive murine local lymph node assay and guinea-pig maximization test.
Contact Dermatitis 60(4) , 193-8, (2009) p-Phenylenediamine (PPD)-related chemicals have been used as antioxidants in rubber products, and many cases of contact dermatitis caused by these chemicals have been reported.The aim of this study was to investigate relative sensitizing potency and cross-rea... |
|
|
Insight into the mechanism of trypanosome lytic factor-1 killing of Trypanosoma brucei brucei.
Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 118(1) , 33-40, (2001) It has been known for almost a century that normal human serum can lyse the extracellular blood parasite Trypanosoma brucei brucei. This process is a result of a non-immune killing factor in human sera known as trypanosome lytic factor (TLF). In this work, we... |
|
|
Antioxidative and apoptotic properties of polyphenolic extracts from edible part of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) on cultured rat hepatocytes and on human hepatoma cells.
Nutr. Cancer 60(2) , 276-83, (2008) Cultured rat hepatocytes and human hepatoma HepG2 cells were used to evaluate the hepatoprotective properties of polyphenolic extracts from the edible part of artichoke (AE). The hepatocytes were exposed to H2O2generated in situ by glucose oxidase and were tr... |
|
|
Phase Separations in Binary and Ternary Cholesterol-Phospholipid Mixtures
Biophys. J. 98(9) , L41-3, (2010) A pair of recent studies has reopened debate on the subject of phase separations in model bilayer mixtures of cholesterol (Chol) and dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine (DPPC). Fluorescence microscopy methods have not been able to detect phase separations in bina... |
|
|
Controlling photochromism between fluoroalkyl end-capped oligomer/polyaniline and N,N'-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine nanocomposites induced by UV-light-responsive titanium oxide nanoparticles.
J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 359(2) , 461-6, (2011) Colloidal stable fluoroalkyl end-capped 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethanesulfonic acid oligomer [R(F)-(MES)(n)-R(F)]/polyaniline[PAn]/TiO(2) nanocomposites and R(F)-(MES)(n)-R(F)/An-dimer (An-dimer: N,N'-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine)/TiO(2) nanocomposites were prepa... |
|
|
Impact of phospholipid bilayer saturation on amyloid-beta protein aggregation intermediate growth: a quartz crystal microbalance analysis.
Anal. Biochem. 399(1) , 30-8, (2010) Evidence that membrane-associated amyloid aggregate growth can impart membrane damage represents one possible mechanism for the neurodegeneration associated with deposited amyloid-beta protein (Abeta) aggregates in the brains of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patie... |
|
|
Design of unsymmetrical azo initiators to increase radical generation efficiency in low-density lipoproteins.
Free Radic. Res. 33(6) , 705-18, (2000) Lipid peroxidation studies often employ the use of azo initiators to produce a slow, steady source of free radicals, but the lack of initiators capable of efficiently generating radicals in lipid regions has created persistent problems in these investigations... |
|
|
Sensitization to para-amino compounds in swim fins in a 10-year-old boy.
J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 7(9) , 770-2, (2009) A ten-year-old boy presented with recurrent eczema on the dorsal of both feet and the thighs. His symptoms became worse when he used racing swim fins. Patch testing included the standard, ointments, preservatives, leather, textile dyes, rubber component, and ... |
|
|
The effect of antioxidant on development of fibrosis by cisplatin in rats.
J. Pharmacol. Sci. 111(4) , 433-9, (2009) Cisplatin causes chronic interstitial disease with fibrosis, but the development mechanism of interstitial fibrosis is not yet understood. We examined the effect of an antioxidant, N,N'-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (DPPD), on development of interstitial fibr... |
|
|
Determination of ammonia based on the electrochemical oxidation of N,N'-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine in propylene carbonate.
Anal. Sci. 23(11) , 1317-20, (2007) The oxidation of N,N'-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (DPPD) has been studied by cyclic voltammetry at glassy carbon electrodes in propylene carbonate. Next, the reaction between ammonia and DPPD was similarly investigated. It has been shown that ammonia revers... |