VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE
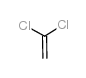
VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE structure
|
Common Name | VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75-35-4 | Molecular Weight | 96.94330 | |
| Density | 1.218 | Boiling Point | 31.2 °C | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H2Cl2 | Melting Point | -122 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | −9 °F | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
A membrane introduction mass spectrometer utilizing ion-molecule reactions for the on-line speciation and quantitation of volatile organic molecules.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 29 , 2187-94, (2015) The ability of membrane introduction mass spectrometry to quantitatively resolve low molecular weight volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene (BTEX) using electron ionization (EI) can be compromised by isobaric inte... |
|
|
The impact of chlorinated solvent co-contaminants on the biodegradation kinetics of 1,4-dioxane.
Chemosphere 91(1) , 88-92, (2013) 1,4-Dioxane (dioxane), a probable human carcinogen, is used as a solvent stabilizer for 1,1,1-trichloroethane (TCA) and other chlorinated solvents. Consequently, TCA and its abiotic breakdown product 1,1-dichloroethene (DCE) are common co-contaminants of diox... |
|
|
Acute, subacute, and subchronic oral toxicity studies of 1,1-dichloroethane in rats: application to risk evaluation.
Toxicol. Sci. 64(1) , 135-45, (2001) 1,1-Dichloroethane (DCE) is a solvent that is often found as a contaminant of drinking water and a pollutant at hazardous waste sites. Information on its short- and long-term toxicity is so limited that the U.S. EPA and ATSDR have not established oral referen... |
|
|
Bioactivation of 1,1-dichloroethylene to its epoxide by CYP2E1 and CYP2F enzymes.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 32(9) , 1032-9, (2004) 1,1-Dichloroethylene (DCE) exposure to mice elicits lung toxicity that selectively targets bronchiolar Clara cells. The toxicity is mediated by DCE metabolites formed via cytochrome P450 metabolism. The primary metabolites formed are DCE epoxide, 2,2-dichloro... |
|
|
Inhaled chemicals may enhance allergic airway inflammation in ovalbumin-sensitised mice.
Toxicology 226(2-3) , 161-71, (2006) Occupational allergy and asthma is a challenging issue in the developing countries. Chemicals inhaled in the workplaces may act not only as allergens but also as immune response modifiers, contributing to asthma exacerbation. In this study, we tested the adju... |
|
|
Differential metabolism of 1,1-dichloroethylene in livers of A/J, CD-1, and C57BL/6 mice.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 29(11) , 1396-402, (2001) 1,1-Dichloroethylene (DCE) causes hepatocellular necrosis that preferentially affects centrilobular hepatocytes. The cytotoxic lesion has been attributed to DCE oxidation mediated mainly by CYP2E1, resulting in formation of reactive intermediates including th... |
|
|
Comparison of pulsed and continuous addition of H2 gas via membranes for stimulating PCE biodegradation in soil columns.
Water Res. 40(6) , 1155-66, (2006) Column experiments were performed to investigate a technology for remediating aquifers contaminated with chlorinated solvents. The technology involves installation of hollow-fiber membranes in the subsurface to supply hydrogen gas (H2) to groundwater to suppo... |
|
|
1,1-dichloroethene as a predominant intermediate of microbial trichloroethene reduction.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 40(6) , 1830-6, (2006) A microbial culture derived from a landfill site in Dover, DE consistently reduced trichloroethene (TCE) to ethene through 1,1-dichloroethene (DCE) as a dominant intermediate in the presence of ampicillin. A constant 1,1-DCE-to-cis-DCE ratio of 2.4 +/- 0.3 wa... |
|
|
Conjugation of glutathione with the reactive metabolites of 1, 1-dichloroethylene in murine lung and liver.
Microsc. Res. Tech. 36(4) , 234-42, (1997) Exposure to 1,1-dichloroethylene (DCE) elicits lung and liver cytotoxicities that are manifested in bronchiolar Clara cell injury and centrilobular necrosis, respectively. The tissue damage is associated with cytochrome P450-dependent bioactivation of DCE to ... |
|
|
Grey-iron foundry slags as reactive media for removing trichloroethylene from groundwater.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(1) , 169-75, (2009) A feasibility study was conducted using slags from six grey-iron foundries to evaluate their potential as reactive media for permeable reactive barriers (PRBs) to remove aqueous trichloroethylene (TCE) from groundwater. Batch tests indicated that the slags ex... |