P-NITROPHENYL-ALPHA-D-MALTOSIDE
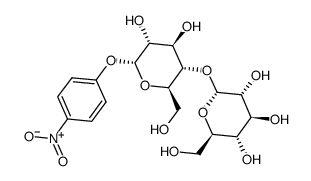
P-NITROPHENYL-ALPHA-D-MALTOSIDE structure
|
Common Name | P-NITROPHENYL-ALPHA-D-MALTOSIDE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 17400-77-0 | Molecular Weight | 463.39000 | |
| Density | 1.7g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 795.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H25NO13 | Melting Point | 145-146℃ (ethanol ligroine ) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 435ºC | |
|
Kinetic characterization of glycosidase activity from disaccharide conjugate to monosaccharide conjugate in Caco-2 cells.
J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 57(5) , 661-4, (2005) Glycosidase activity influences the intestinal absorption of glycosides. Our previous study in rats suggested that disaccharide conjugates might be prototypes for pre-prodrugs aiming at the Na(+)/glucose co-transporter-mediated transport of prodrugs (drug glu... |
|
|
Effect of a p-nitro group of phenyl-maltooligosaccharide substrate on the change of action specificity of lysine-modified porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase.
Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 35(1) , 79-85, (1995) The effect of chemical modification of lysine residues on the activity of porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase (PPA) was examined, using p-nitrophenyl-alpha-D-maltoside, p-nitrophenyl-alpha-D-maltotrioside, phenyl-alpha-D-maltoside and phenyl-alpha-D-maltotriosid... |
|
|
Rapid determination of alpha-amylase activity by use of a new chromogenic substrate.
Clin. Chem. 33(4) , 524-8, (1987) A new chromogenic substrate that is blocked at the nonreducing end, 4,6-benzylidene-alpha-D-4-nitrophenylmaltoheptaoside, is used to determine alpha-amylase (EC 3.2.1.1) activity in serum in a coupled assay with alpha-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.20) and glucoamylas... |
|
|
Barley malt-alpha-amylase. Purification, action pattern, and subsite mapping of isozyme 1 and two members of the isozyme 2 subfamily using p-nitrophenylated maltooligosaccharide substrates.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1159(2) , 193-202, (1992) Isoforms AMY1, AMY2-1 and AMY2-2 of barley alpha-amylase were purified from malt. AMY2-1 and AMY2-2 are both susceptible to barley alpha-amylase/subtilisin inhibitor. The action of these isoforms is compared using substrates ranging from p-nitrophenylmaltosid... |
|
|
Differential rate assay of human pancreatic and salivary alpha-amylases in serum using two coupled enzymes.
J. Biochem. 100(5) , 1353-8, (1986) p-Nitrophenyl O-6-deoxy-6-[(2-pyridyl)amino]-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1----4)-O-alpha- D-glucopyranosyl-(1----4)-O-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1----4)-O-alpha-D- glucopyranosyl-(1----4)-alpha-D-glucopyranoside (FG5P) is hydrolyzed by human pancreatic a-amylase (HP... |
|
|
Differentiation of human non-salivary, non-pancreatic alpha-amylase from salivary and pancreatic alpha-amylases by use of FG5P.
J. Biochem. 107(4) , 546-9, (1990) Human non-salivary, non-pancreatic alpha-amylase (yHXA) is the gene product of a newly found human alpha-amylase gene expressed in yeast. Its mode of action on a fluorogenic derivative of p-nitrophenyl alpha-maltopentaoside, FG5P (FG-G-G-G-G-P), was examined ... |
|
|
Contributions of phenylalanine 335 to ligand recognition by human surfactant protein D: ring interactions with SP-D ligands.
J. Biol. Chem. 281(26) , 18008-14, (2006) Surfactant protein D (SP-D) is an innate immune effector that contributes to antimicrobial host defense and immune regulation. Interactions of SP-D with microorganisms and organic antigens involve binding of glycoconjugates to the C-type lectin carbohydrate r... |
|
|
The roles of histidine residues at the starch-binding site in streptococcal-binding activities of human salivary amylase.
Arch. Oral Biol. 44(2) , 119-27, (1999) Human salivary alpha-amylase participates in the initial digestion of starch and may be involved in the colonization of viridans streptococci in the mouth. To elucidate the role of histidine residues located near the starch-binding site on the streptococcal-b... |
|
|
Transport of p-nitrophenyl-alpha-maltoside by the maltose transport system of Escherichia coli and its subsequent hydrolysis by a cytoplasmic alpha-maltosidase.
J. Bacteriol. 165(3) , 918-22, (1986) In wild-type Escherichia coli the activity of the maltose transport system is dependent on a periplasmic maltose-binding protein. It has been possible, however, to isolate mutants in which transport activity is mediated by the membrane components of the syste... |
|
|
Reference values for alpha-amylase activity in serum and urine by a new chromogenic amylase method.
Ric. Clin. Lab. 14(3) , 439-42, (1984)
|