Lutein
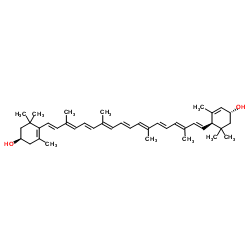
Lutein structure
|
Common Name | Lutein | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 127-40-2 | Molecular Weight | 568.871 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 702.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C40H56O2 | Melting Point | 183℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 269.1±27.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Effects of UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic composition of leaves and berries of Vitis vinifera cv. Graciano.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(2) , 409-16, (2014) Ultraviolet (UV) radiation induces adaptive responses that can be used for plant production improvement. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of solar UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic compounds of leaves and berry skins of Vitis vinifera ... |
|
|
Nutrients value and antioxidant content of indigenous vegetables from Southern Thailand.
Food Chem. 173 , 838-46, (2014) Evidence from epidemiological studies has strongly suggested that diets rich in fruits and vegetables play a vital role in disease prevention. The aim of this study was to determine nutrient and antioxidant content for 15 varieties of indigenous vegetables an... |
|
|
Phenolic and carotenoid profiles and antiproliferative activity of foxtail millet.
Food Chem. 174 , 495-501, (2014) Commonly consumed foxtail millet varieties Jingu28 and Jingu34 were compared in terms of phytochemical composition, antioxidant property, and antiproliferative activity. The cellular antioxidant activity (CAA) was evaluated based on HepG2 cell cultivation. An... |
|
|
The effect of dietary supplementation with the natural carotenoids curcumin and lutein on broiler pigmentation and immunity.
Poult. Sci. 92(5) , 1177-85, (2013) The objective of this study was to compare the effects of supplementation with 2 carotenoids, curcumin and lutein, on pigmentation and immunity in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated broiler chicks. Two hundred forty 1-d-old Arbor Acres broilers were randomly... |
|
|
Optimal extraction and fingerprinting of carotenoids by accelerated solvent extraction and liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry.
Food Chem. 177 , 369-75, (2015) Accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) is applied for the extraction of carotenoids from orange carrot and the extraction parameters were optimized. Two carotenoids, lutein and β-carotene, are selected as the validation process. Hildebrand solubility parameters... |
|
|
Lesion simulating disease 1 and enhanced disease susceptibility 1 differentially regulate UV-C-induced photooxidative stress signalling and programmed cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Plant Cell Environ. 38(2) , 315-30, (2015) As obligate photoautotrophs, plants are inevitably exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Because of stratospheric ozone depletion, UV has become more and more dangerous to the biosphere. Therefore, it is important to understand UV perception and signal trans... |
|
|
An improved UHPLC-UV method for separation and quantification of carotenoids in vegetable crops.
Food Chem. 165 , 475-82, (2014) Carotenoid identification and quantitation is critical for the development of improved nutrition plant varieties. Industrial analysis of carotenoids is typically carried out on multiple crops with potentially thousands of samples per crop, placing critical ne... |
|
|
Chemical Compositions of Egg Yolks and Egg Quality of Laying Hens Fed Prebiotic, Probiotic, and Synbiotic Diets.
J. Food Sci. 80 , C1686-95, (2015) A 16-wk feeding experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of a prebiotic, isomaltooligosaccharide (IMO), a probiotic, PrimaLac®, and their combination as a synbiotic on the chemical compositions of egg yolks and the egg quality of laying hens. One h... |
|
|
Carotenoid bioaccessibility in pulp and fresh juice from carotenoid-rich sweet oranges and mandarins.
Food Funct. 6 , 1950-9, (2015) Citrus fruits are a good source of carotenoids for the human diet; however, comparative studies of carotenoids in different citrus food matrices are scarce. In this work the concentration and bioaccessibility of carotenoids in sweet oranges and mandarins with... |
|
|
Longitudinal Survey of Carotenoids in Human Milk from Urban Cohorts in China, Mexico, and the USA.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0127729, (2015) Emerging evidence indicates that carotenoids may have particular roles in infant nutrition and development, yet data on the profile and bioavailability of carotenoids from human milk remain sparse. Milk was longitudinally collected at 2, 4, 13, and 26 weeks p... |