PYRITE
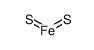
PYRITE structure
|
Common Name | PYRITE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 12068-85-8 | Molecular Weight | 119.97500 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | FeS2 | Melting Point | 1171ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Molybdenum(VI) removal by using constructed wetlands with different filter media and plants.
Water Sci. Technol. 67(8) , 1859-66, (2013) The efficacy and capacity of vertical-flow wetland filters on molybdenum (Mo) removal from wastewater was examined, employing reed (Phragmites australis) and cattail (Typha latifolia) as well as different adsorption granular media. Humus, cinder, modified cin... |
|
|
[Oxidation of sulfur-containing substrates by aboriginal and experimentally designed microbial communities].
Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 48(6) , 640-5, (2012) Aboriginal and experimental (constructed of pure microbial cultures) communities of acidophilic chemolithotrophs have been studied. The oxidation of elemental sulfur, sodium thiosulfate, and potassium tetrathionate as sole sources of energy has been monitored... |
|
|
Metal solubilization from powdered printed circuit boards by microbial consortium from bauxite and pyrite ores.
Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 49(3) , 279-84, (2013) With the current rapid developments in technology, there is an increasing accumulation of outdated electronic equipment. The primary reason for this increase is the low rate of recycling due to the complex nature of such waste. Bioleaching offers a promising ... |
|
|
Microbial community potentially responsible for acid and metal release from an Ostrobothnian acid sulfate soil.
FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 84(3) , 555-63, (2013) Soils containing an approximately equal mixture of metastable iron sulfides and pyrite occur in the boreal Ostrobothnian coastal region of Finland, termed 'potential acid sulfate soil materials'. If the iron sulfides are exposed to air, oxidation reactions re... |
|
|
Silane-based coatings on the pyrite for remediation of acid mine drainage.
Water Res. 47(13) , 4391-402, (2013) Acid mine drainage (AMD) resulting from the oxidation of pyrite and other metal sulfides has caused significant environmental problems, including acidification of rivers and streams as well as leaching of toxic metals. With the goal of controlling AMD at the ... |
|
|
Specific jarosite biomineralization by Purpureocillium lilacinum, an acidophilic fungi isolated from Río Tinto.
Environ. Microbiol. 15(8) , 2228-37, (2013) Río Tinto (Huelva, southwestern Spain) is an extreme environment with a remarkably constant acidic pH and a high concentration of heavy metals, conditions generated by the metabolic activity of chemolithotrophic microorganisms thriving in the rich complex sul... |
|
|
Soluble microbial products decrease pyrite oxidation by ferric iron at pH < 2.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(15) , 8658-65, (2013) Research on microbial activity in acid mine drainage (AMD) has focused on transformations of iron and sulfur. However, carbon cycling, including formation of soluble microbial products (SMP) from cell growth and decay, is an important biogeochemical component... |
|
|
Long term geological record of a global deep subsurface microbial habitat in sand injection complexes.
Sci. Rep. 3 , 1828, (2013) There is extensive evidence from drilling into continental margins for microbial colonization of a deep biosphere. However it is difficult to prove deep biosphere activity in the geological record, where evidence for life is dominated by the remains of organi... |
|
|
Acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt: 1. Hydrochemical characteristics and pollutant load of the Tinto and Odiel rivers.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 20(11) , 7509-19, (2013) Acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt is probably the worst case in the world of surface water pollution associated with mining of sulphide mineral deposits. The Iberian Pyrite Belt is located in SW Iberian Peninsula, and it has been mined during the ... |
|
|
Inflammatory stress response in A549 cells as a result of exposure to coal: evidence for the role of pyrite in coal workers' pneumoconiosis pathogenesis.
Chemosphere 93(6) , 1216-21, (2013) On the basis of a recent epidemiological study it is hypothesized that pyrite content in coal is an important factor in coal workers' pneumoconiosis (CWP) pathogenesis. While the role of pyrite in pathogenesis remains to be resolved, the ability of the minera... |