Ibrolipim
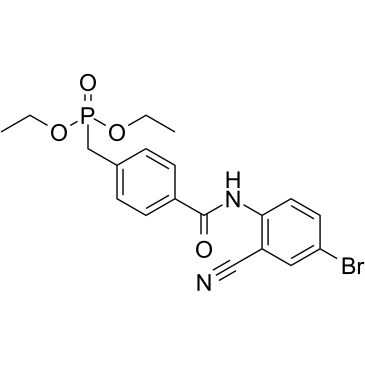
Ibrolipim structure
|
Common Name | Ibrolipim | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 133208-93-2 | Molecular Weight | 451.25100 | |
| Density | 1.44g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 512.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H20BrN2O4P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 263.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Effects of NO-1886 on inflammation-associated cytokines in high-fat/high-sucrose/high-cholesterol diet-fed miniature pigs.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 540(1-3) , 139-46, (2006) Inflammation, closely associated with obesity, is emerging as an important risk factor for the pathophysiological development of atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus. Fat balance is critical in the aetiology of obesity. Lipoprotein lipase is an important enz... |
|
|
NO-1886 suppresses diet-induced insulin resistance and cholesterol accumulation through STAT5-dependent upregulation of IGF1 and CYP7A1.
J. Endocrinol. 1st ed., 204 , 47-56, (2010) Insulin resistance and dyslipidemia are both considered to be risk factors for metabolic syndrome. Low levels of IGF1 are associated with insulin resistance. Elevation of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) concomitant with depression of high-density ... |
|
|
Evaluation of induction potency of new drug candidates on CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 using real-time one-step RT-PCR in primary cultures of cryopreserved human hepatocytes.
Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 24(5) , 446-50, (2009) This study evaluates the induction potency of new drug candidates on mRNA levels of CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 in primary cultures of cryopreserved human hepatocytes. Analysis was performed by quantitative real-time RT-PCR using primers and TaqMan probes. Positive con... |
|
|
NO-1886 (ibrolipim), a lipoprotein lipase-promoting agent, accelerates the expression of UCP3 messenger RNA and ameliorates obesity in ovariectomized rats.
Metab. Clin. Exp. 55(2) , 151-8, (2006) The synthetic compound NO-1886 (ibrolipim, [4-(4-bromo-2-cyano-phenylcarbamoyl)-benzyl]-phosphonic acid diethyl ester, CAS 133208-93-2) is a lipoprotein lipase (LPL)-promoting agent that decreases plasma triglycerides, increases high-density lipoprotein chole... |
|
|
NO-1886, a lipoprotein lipase activator, attenuates vascular smooth muscle contraction in rat aorta.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 554(2-3) , 183-90, (2007) The chemical compound [4-(4-bromo-2-cyano-phenylcarbamoyl)-benzyl]-phosphonic acid diethyl ester (NO-1886) is a lipoprotein lipase activator having beneficial effects on both diabetes control and the cardiovascular system. Preventing accumulation of lipids in... |
|
|
NO-1886 ameliorates glycogen metabolism in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells by GSK-3β signalling.
J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 64(2) , 293-301, (2012) The aim of the study was to elucidate the possible role and mechanism of NO-1886 (ibrolipim, a lipoprotein lipase activator) in ameliorating insulin resistance induced by high palmitate.HepG2 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium and were treated with palmi... |
|
|
Preventive effect of Ibrolipim on suppressing lipid accumulation and increasing lipoprotein lipase in the kidneys of diet-induced diabetic minipigs.
Lipids Health Dis. 10 , 117, (2011) The role of renal lipoprotein lipase (LPL) per se in kidney diseases is still controversial and obscure. The purpose of this study was to observe the preventive effects of Ibrolipim, a LPL activator, on lipid accumulation and LPL expression in the kidneys of ... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of NO-1886, a lipoprotein lipase-promoting agent, in cynomolgus monkey.
Xenobiotica 33(12) , 1247-60, (2003) 1. The study was conducted to investigate the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of NO-1886 (diethyl 4-[(4-bromo-2-cyanophenyl) carbamoyl] benzylphosphonate) in cynomolgus monkeys. 2. After single intravenous administration of NO-1886 at a dose of 3 mg kg(-1), t... |
|
|
Ibrolipim attenuates high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells via PI3K/Akt pathway.
Pharmazie 66(10) , 798-803, (2011) Endothelial dysfunction is a key event in the onset and progression of atherosclerosis associated with diabetes. Increasing cell apoptosis may lead to endothelial dysfunction and contribute to vascular complications. Therefore, we aimed to elucidate the possi... |
|
|
Pharmacological approaches to modifying HDL: more basic science to understand HDL metabolism is necessary. Editorial to: "NO-1886 up-regulates Niemann-Pick C1 protein (NPC1) expression through liver X receptor alpha signaling pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells" by Xin Ma et al.
Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 23(3) , 187-8, (2009)
|