| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
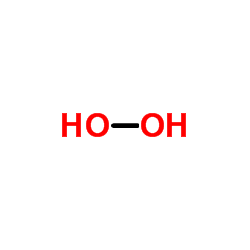 |
Hydrogen peroxide
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
 |
Fructose
CAS:57-48-7 |
|
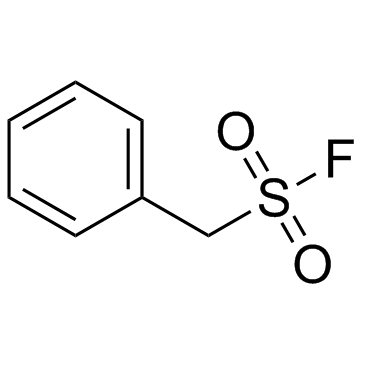 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
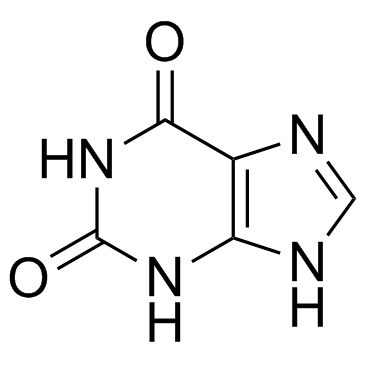 |
2,6-Dihydroxypurine
CAS:69-89-6 |
|
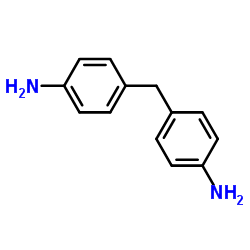 |
4,4′-methylenedianiline
CAS:101-77-9 |
|
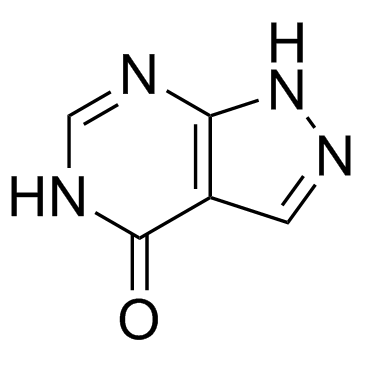 |
Allopurinol
CAS:315-30-0 |
|
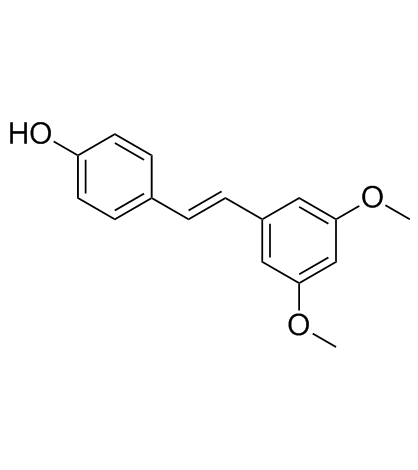 |
pterostilbene
CAS:537-42-8 |
|
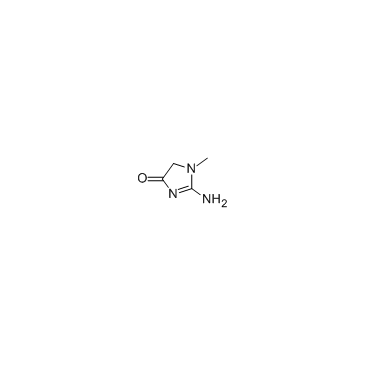 |
Creatinine
CAS:60-27-5 |