| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
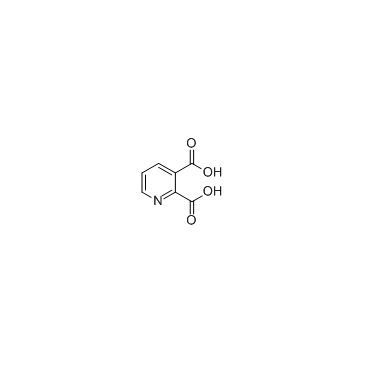 |
Quinolinic acid
CAS:89-00-9 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
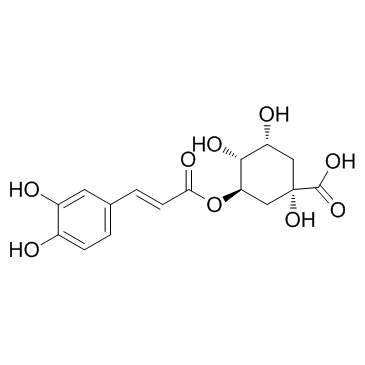 |
Chlorogenic acid
CAS:327-97-9 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
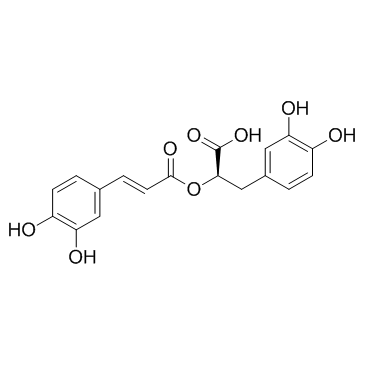 |
Rosmarinic acid
CAS:20283-92-5 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
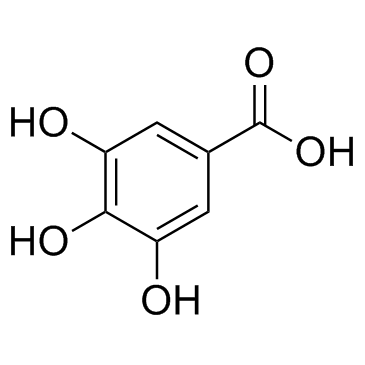 |
Gallic acid
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
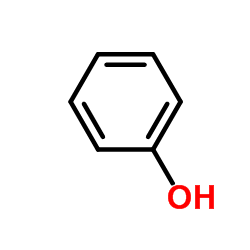 |
Phenol
CAS:108-95-2 |