| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Atropine sulfate monohydrate
CAS:5908-99-6 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Ethanoic anhydride
CAS:108-24-7 |
|
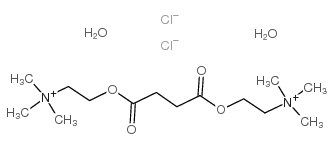 |
Succinylcholine Chloride Dihydrate
CAS:6101-15-1 |
|
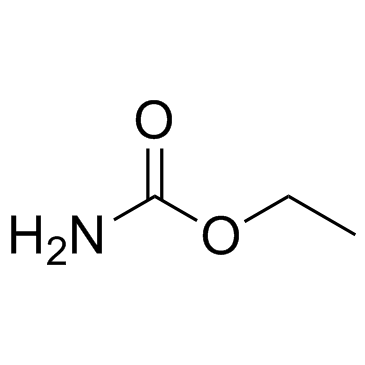 |
Urethane
CAS:51-79-6 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
Apamin
CAS:24345-16-2 |
|
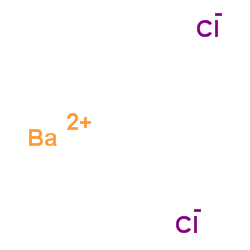 |
barium chloride
CAS:10361-37-2 |
|
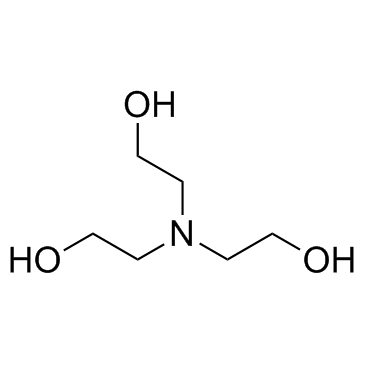 |
Triethanolamine
CAS:102-71-6 |
|
 |
capsaicin
CAS:404-86-4 |