| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
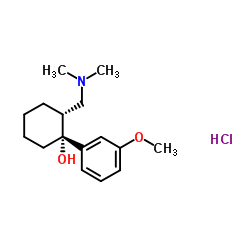 |
Tramadol hydrochloride
CAS:36282-47-0 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
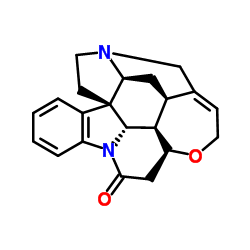 |
(−)-Strychnine
CAS:57-24-9 |
|
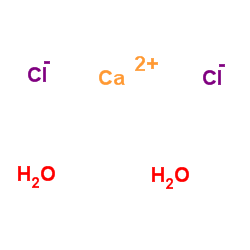 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
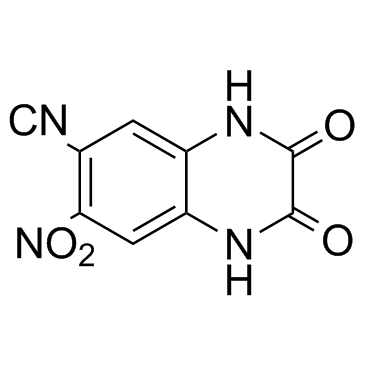 |
CNQX
CAS:115066-14-3 |
|
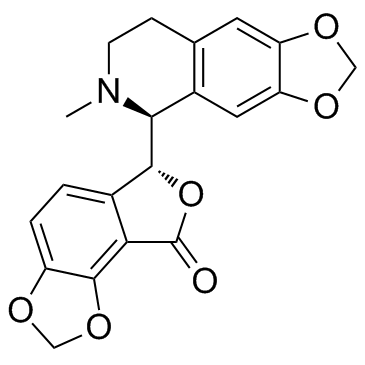 |
(+)-Bicuculline
CAS:485-49-4 |