(+)-Bicuculline
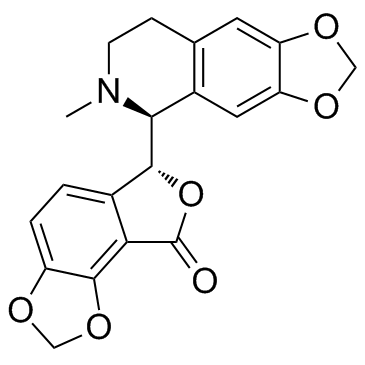
(+)-Bicuculline structure
|
Common Name | (+)-Bicuculline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 485-49-4 | Molecular Weight | 367.352 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 542.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H17NO6 | Melting Point | 196-198 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 281.8±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Radixin regulates synaptic GABAA receptor density and is essential for reversal learning and short-term memory.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6872, (2015) Neurotransmitter receptor density is a major variable in regulating synaptic strength. Receptors rapidly exchange between synapses and intracellular storage pools through endocytic recycling. In addition, lateral diffusion and confinement exchanges surface me... |
|
|
Reduced SNAP-25 increases PSD-95 mobility and impairs spine morphogenesis.
Cell Death Differ. 22 , 1425-36, (2015) Impairment of synaptic function can lead to neuropsychiatric disorders collectively referred to as synaptopathies. The SNARE protein SNAP-25 is implicated in several brain pathologies and, indeed, brain areas of psychiatric patients often display reduced SNAP... |
|
|
Forebrain NR2B overexpression enhancing fear acquisition and long-term potentiation in the lateral amygdala.
Eur. J. Neurosci. 42 , 2214-23, (2015) N-methyl-d-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor-dependent long-term potentiation (LTP) at the thalamus-lateral amygdala (T-LA) synapses is the basis for acquisition of auditory fear memory. However, the role of the NMDA receptor NR2B subunit in synaptic plasticity a... |
|
|
Differential effects of N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate on synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors are subunit- and pH-dependent in the CA1 region of the mouse hippocampus.
Neurobiol. Dis. 82 , 580-92, (2015) Ischemic strokes cause excessive release of glutamate, leading to overactivation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and excitotoxicity-induced neuronal death. For this reason, inhibition of NMDARs has been a central focus in identifying mechanisms to ... |
|
|
Artemisia capillaris Thunberg Produces Sedative-Hypnotic Effects in Mice, Which are Probably Mediated Through Potentiation of the GABAA Receptor.
Am. J. Chin. Med. 43 , 667-79, (2015) The Artemisia group of plants has long been used as a traditional remedy for various conditions. The present study assessed the sleep-promoting (sedative-hypnotic) effects of Artemisia capillaris Thunberg (A. capillaris), and elucidated a possible mechanism b... |
|
|
Anatomical and electrophysiological changes in striatal TH interneurons after loss of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway.
Brain Struct. Funct. 220(1) , 331-49, (2015) Using transgenic mice that express enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) under the control of the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) promoter, we have previously shown that there are approximately 3,000 striatal EGFP-TH interneurons per hemisphere in mice. Here, w... |
|
|
Involvement of neurotransmitters in the action of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide-receptor system on passive avoidance learning in rats.
Neurochem. Res. 39(8) , 1477-83, (2014) The nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide (NOP) receptor and its endogenous ligand plays role in several physiologic functions of the central nervous system, including pain, locomotion, anxiety and depression, reward and drug addiction, learning and memory. Previous... |
|
|
Neurotransmitter-mediated anxiogenic action of PACAP-38 in rats.
Behav. Brain Res. 281 , 333-8, (2015) The action of PACAP-38 was studied by measuring the anxiogenic-anxiolytic behavior of rats in an elevated plus maze. PACAP-38 was administered into the lateral brain ventricle and the behavior of the animals was measured 3h later. The possible involvement of ... |
|
|
Pathophysiological mechanisms underlying increased anxiety after soman exposure: reduced GABAergic inhibition in the basolateral amygdala.
Neurotoxicology 44 , 335-43, (2014) The recent sarin attack in Syria killed 1429 people, including 426 children, and left countless more to deal with the health consequences of the exposure. Prior to the Syrian chemical assault, nerve agent attacks in Japan left many victims suffering from neur... |
|
|
Effects of tramadol on substantia gelatinosa neurons in the rat spinal cord: an in vivo patch-clamp analysis.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0125147, (2015) Tramadol is thought to modulate synaptic transmissions in the spinal dorsal horn mainly by activating µ-opioid receptors and by inhibiting the reuptake of monoamines in the CNS. However, the precise mode of modulation remains unclear. We used an in vivo patch... |