| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
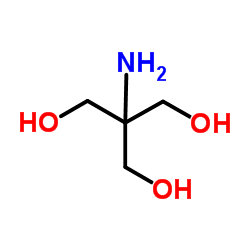 |
Trometamol
CAS:77-86-1 |
|
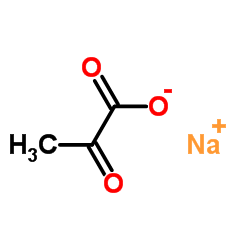 |
Sodium 2-oxopropanoate
CAS:113-24-6 |
|
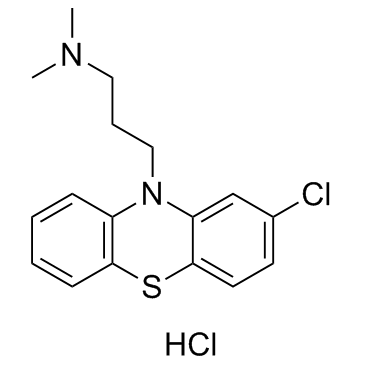 |
Chlorpromazine hydrochloride
CAS:69-09-0 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
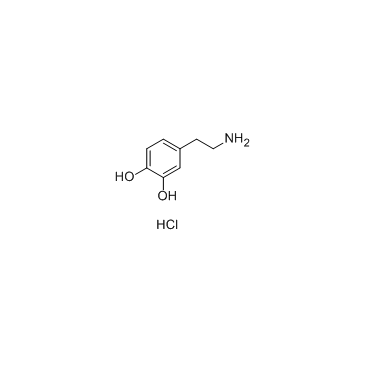 |
Dopamine hydrochloride
CAS:62-31-7 |
|
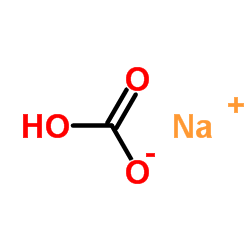 |
SodiuM bicarbonate
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |