| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
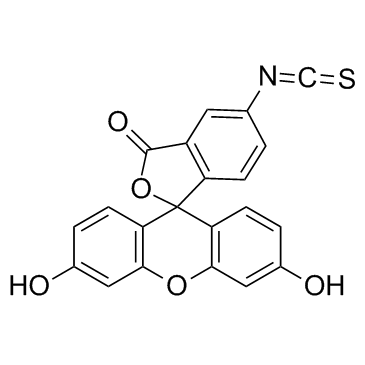 |
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
CAS:3326-32-7 |
|
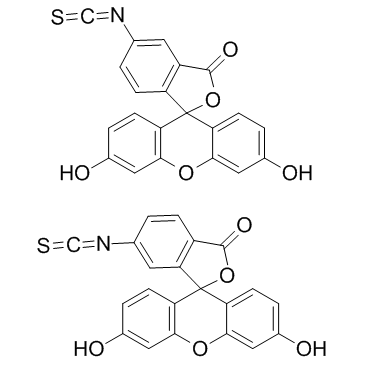 |
fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate
CAS:27072-45-3 |
|
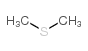 |
dms
CAS:75-18-3 |
|
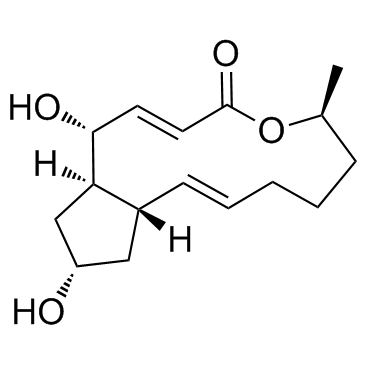 |
Brefeldin A
CAS:20350-15-6 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
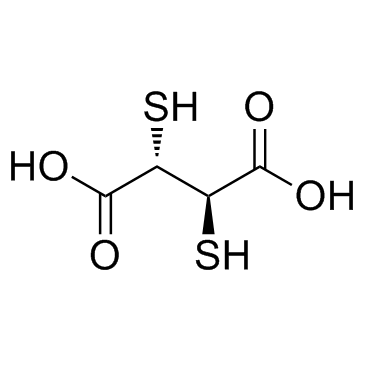 |
Succimer
CAS:304-55-2 |
|
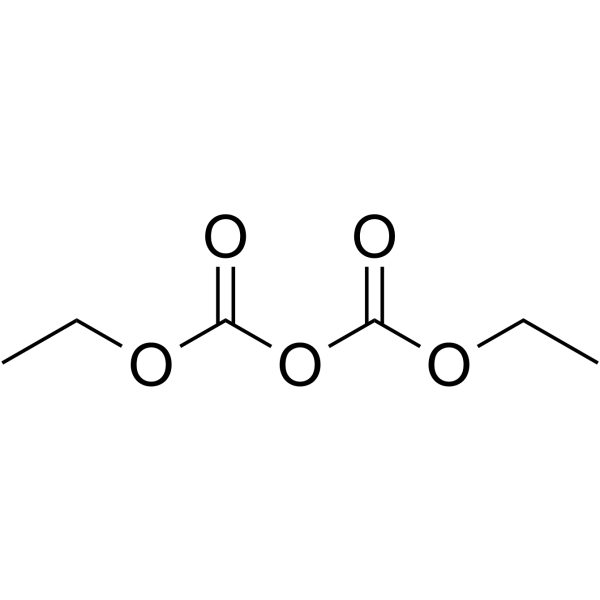 |
Diethyl pyrocarbonate
CAS:1609-47-8 |
|
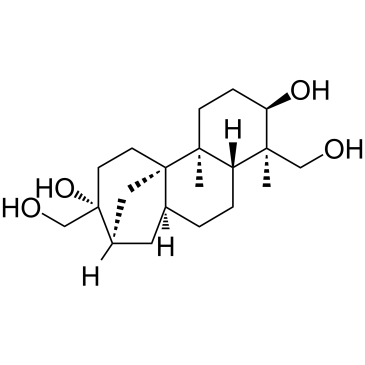 |
(+)-Aphidicolin
CAS:38966-21-1 |