| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
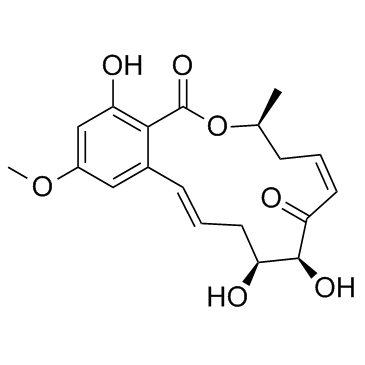 |
5Z-7-Oxozeaenol
CAS:253863-19-3 |
|
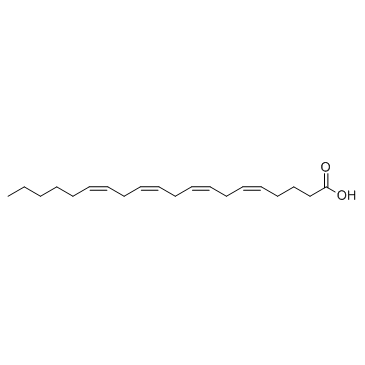 |
Arachidonic acid
CAS:506-32-1 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
Aspirin
CAS:50-78-2 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
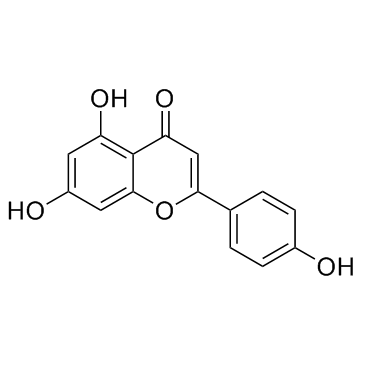 |
Apigenin
CAS:520-36-5 |
|
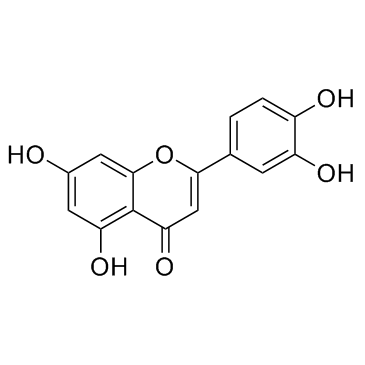 |
Luteolin
CAS:491-70-3 |
|
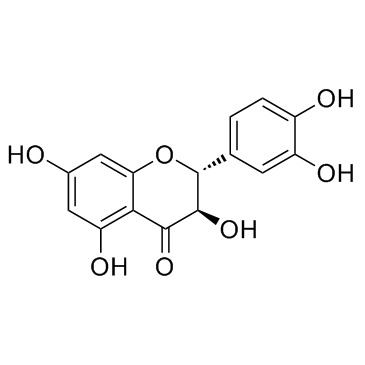 |
Taxifolin
CAS:480-18-2 |
|
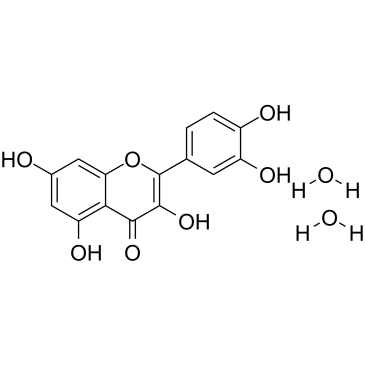 |
Quercetin dihydrate
CAS:6151-25-3 |