| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
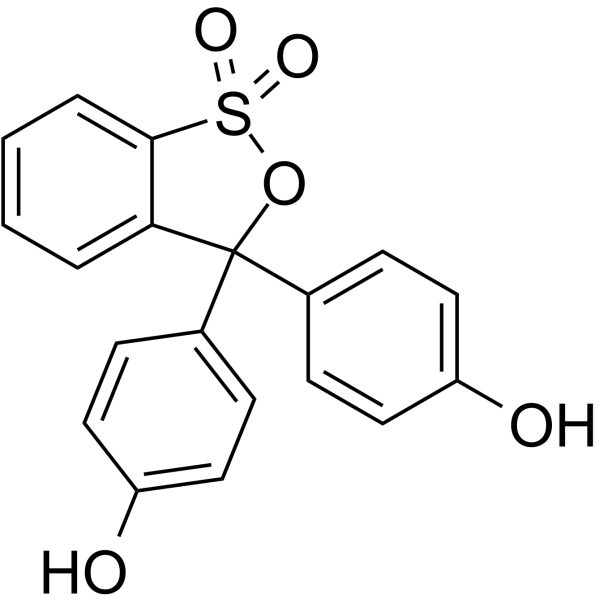 |
Phenol red
CAS:143-74-8 |
|
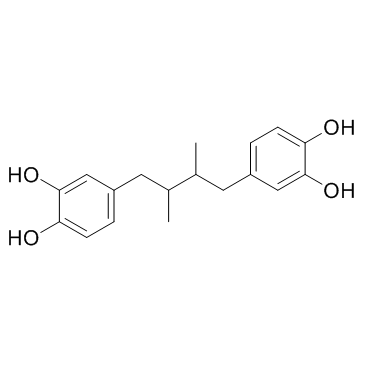 |
Nordihydroguaiaretic acid
CAS:500-38-9 |
|
 |
Acid Red 87
CAS:17372-87-1 |
|
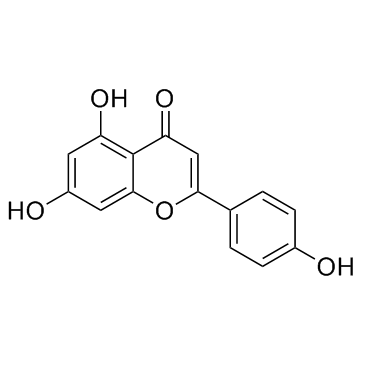 |
Apigenin
CAS:520-36-5 |
|
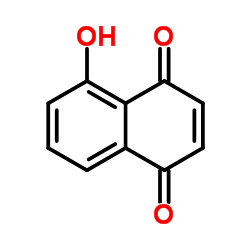 |
Juglone
CAS:481-39-0 |
|
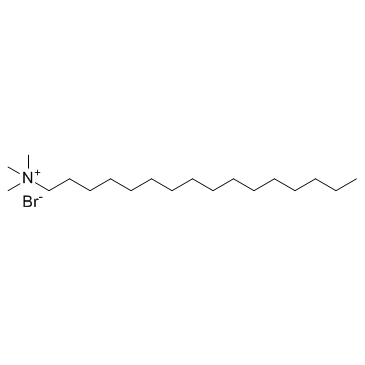 |
Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
CAS:57-09-0 |
|
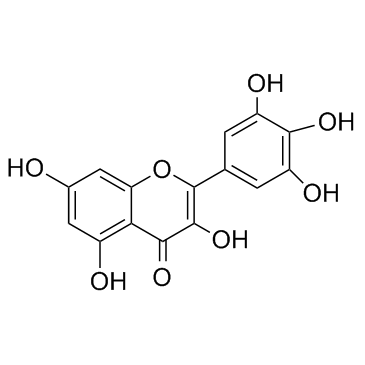 |
Myricetin
CAS:529-44-2 |
|
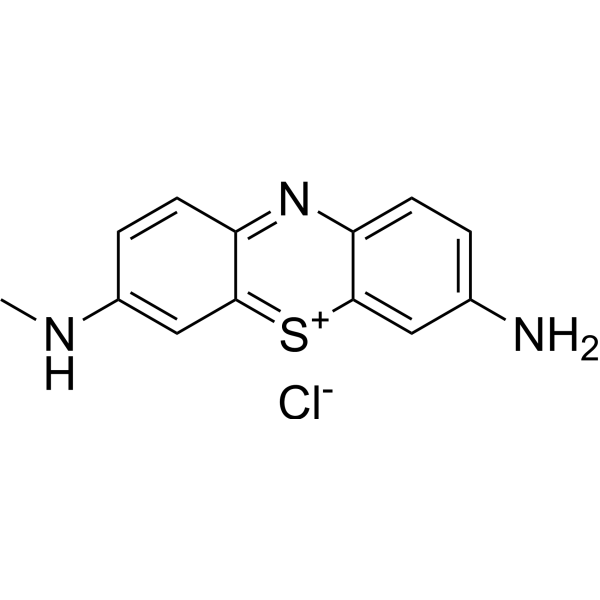 |
3-Amino-7-(methylamino)phenothiazin-5-ium chloride
CAS:531-57-7 |
|
 |
Thiophane
CAS:110-01-0 |
|
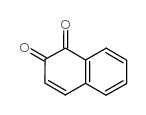 |
1,2-NAPHTHOQUINONE
CAS:524-42-5 |