| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
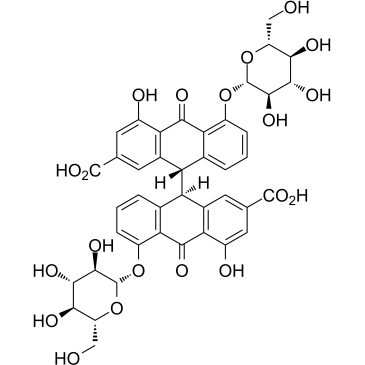 |
Sennoside B
CAS:128-57-4 |
|
 |
Sennoside A
CAS:81-27-6 |
|
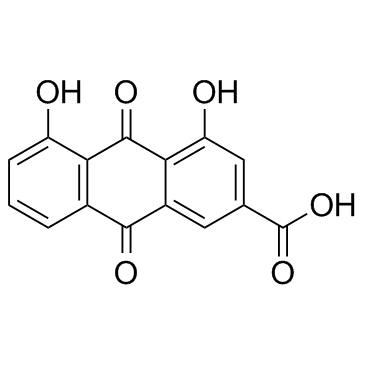 |
Rhein
CAS:478-43-3 |
|
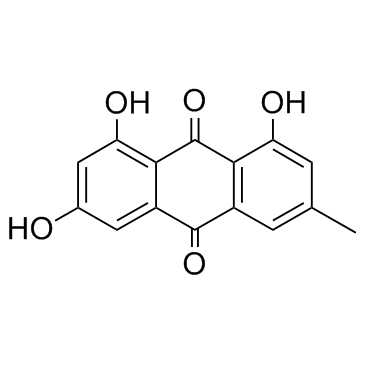 |
Emodin
CAS:518-82-1 |