| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
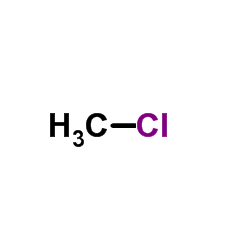 |
Chloromethane
CAS:74-87-3 |
|
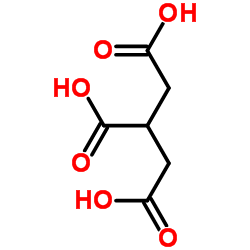 |
Tricarballylic acid
CAS:99-14-9 |
|
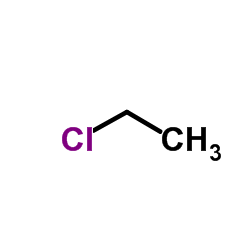 |
monochloroethane
CAS:75-00-3 |
|
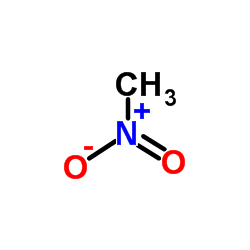 |
nitromethane
CAS:75-52-5 |