| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
trans-4-Hydroxycinnamic acid
CAS:501-98-4 |
|
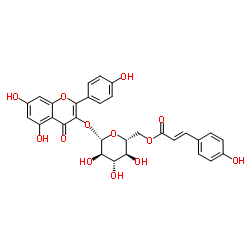 |
tiliroside
CAS:20316-62-5 |
|
 |
Kaempferol
CAS:520-18-3 |