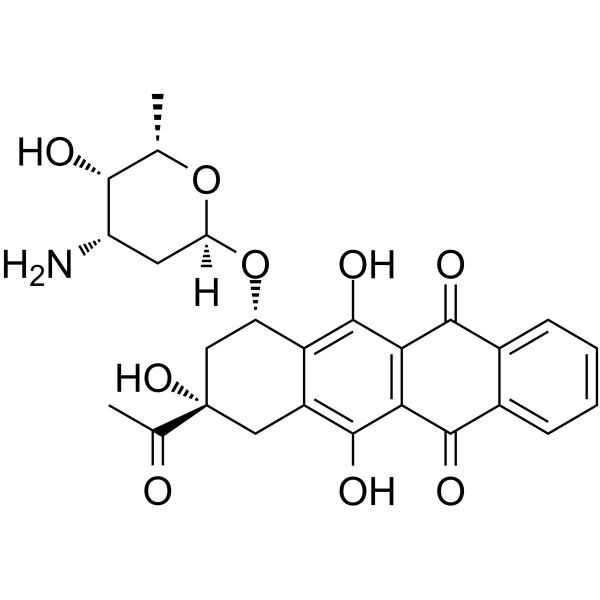
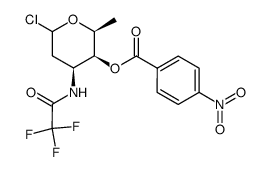
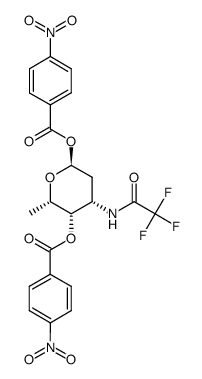
58957-92-9
| Name | idarubicin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(7S-cis)-9-Acetyl-7-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,9,11-trihydroxy-5,12-naphthacenedione
(1S,3S)-3-Acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside Idarubicine Idarubicina EINECS 260-990-7 4-Demethoxydaunomycin Idarubicine [INN-French] 5,12-naphthacenedione Idamycin Idarubicinum 4-Demethoxydaunorubicin Idarubicinum [INN-Latin] Idarubicin MFCD00866457 (7S,9S)-9-acetyl-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6,9,11-trihydroxy-8,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5,12-dione (1S,3S)-3-Acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-1-tetracenyl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside |
| Description | Idarubicin is an orally active and potent anthracycline antileukemic agent. Idarubicin inhibits the topoisomerase II interfering with the replication of DNA and RNA transcription. Idarubicin shows induction of DNA damage. Idarubicin inhibits DNA synthesis and of c-myc expression. Idarubicin inhibits the growth of bacteria and yeasts[1][2][3][4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase II |
| In Vitro | The IC50 of idarubicin is 3.3 ± 0.4 ng/mL on MCF-7 monolayers and 7.9 ± 1.1 ng/mL in multicellular spheroids[1]. Idarubicin shows a greater cytotoxicity than daunorubicin or doxorubicin in various in vitro systems. This has been attributed to a better ability of idarubicin to induce the formation of topoisomerase II -mediated DNA breaks[2]. Idarubicin is about 57.5-fold and 25-fold more active than doxorubicin and epirubicin, respectively[3]. Idarubicin produces a concentration-dependent reduction in MCF-7 cell growth, with an IC50 of approximately 0.01 μM. Idarubicin produces a concentration-dependent inhibition of DNA synthesis and a time- and concentration-dependent suppression of c-myc expression[4]. |
| References |
[2]. Robert J. Clinical pharmacokinetics of idarubicin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993 Apr;24(4):275-88. |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 725.4±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C26H27NO9 |
| Molecular Weight | 497.494 |
| Flash Point | 392.5±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 497.168579 |
| PSA | 176.61000 |
| LogP | 2.95 |
| Appearance | solid |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.706 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | 60-61-28-40 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | HB7877000 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |