151096-09-2
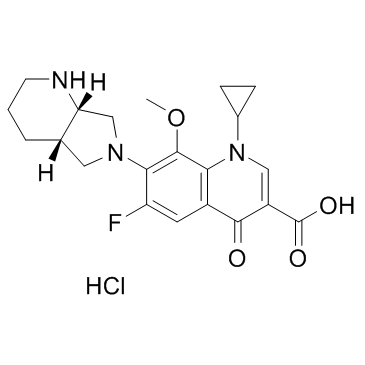
| Name | moxifloxacin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
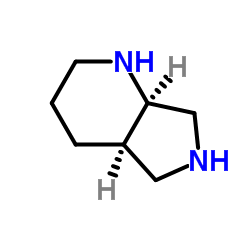
1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-[(4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-((4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid MAXIOFFOXACIN BAY 12-8039 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-[(4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid Moxifloxacin Moxeza Avdox Vigamox Avelox Avalox MFCD04117996 |
| Description | Moxifloxacin is a synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic agent.Target: AntibacterialMoxifloxacin is an extended-spectrum fluoroquinolone which has improved coverage against gram-positive cocci and atypical pathogens compared with older fluoroquinolone agents, while retaining good activity against gram-negative bacteria. The antibacterial spectrum of moxifloxacin includes all major upper and lower respiratory tract pathogens; it is one of the most active fluoroquinolones against pneumococci, including penicillin- and macrolide-resistant strains [1]. Moxifloxacin has limited phototoxic potential. In clinical trials, moxifloxacin had clinical success rates of 88-97% and bacteriologic eradication rates of 90-97%. Moxifloxacin is a safe and effective antimicrobial that will be useful for treating acute sinusitis, acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, and community-acquired pneumonia [2]. Moxifloxacin possibly stimulates lipid peroxidation and enhances phagocytosis, as depicted by MDA production and survival prolongation, without being toxic as depicted by white blood cell count [3]. Clinical indications: Abdominal abscess; Acute bronchitis; Acute sinusitis; Bacterial infectionToxicity: Symptoms of overdose include CNS and gastrointestinal effects such as decreased activity, somnolence, tremor, convulsions, vomiting, and diarrhea. The minimal lethal intravenous dose in mice and rats is 100 mg/kg. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 636.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 193-195 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C21H24FN3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 401.43 |
| Flash Point | 338.7±31.5 °C |
| PSA | 83.80000 |
| LogP | 1.60 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.633 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29329970 |
|
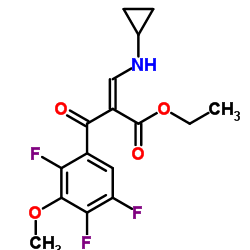
~89% 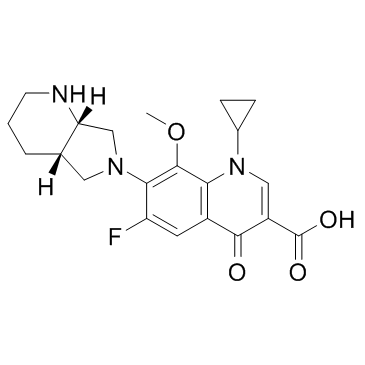
151096-09-2 |
| Literature: SANDOZ AG Patent: EP1992626 A1, 2008 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 10 ; |
|
~% 
151096-09-2 |
| Literature: WO2008/59521 A2, ; Page/Page column 26 ; |
|
~% 
151096-09-2 |
| Literature: WO2008/59521 A2, ; Page/Page column 23 ; |
|
~% 
151096-09-2 |
| Literature: WO2008/59521 A2, ; Page/Page column 23 ; |
|
~% 
151096-09-2 |
| Literature: WO2008/59521 A2, ; Page/Page column 23 ; |
|
~% 
151096-09-2 |
| Literature: WO2008/59521 A2, ; Page/Page column 22; 23-24 ; |
|
~% 
151096-09-2 |
| Literature: WO2008/59223 A2, ; Page/Page column 15-16 ; |
|
~% 
151096-09-2 |
| Literature: US5480879 A1, ; |
|
~% 
151096-09-2 |
| Literature: Spectrochimica Acta - Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, , vol. 121, p. 254 - 258 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 29329970 |
|---|